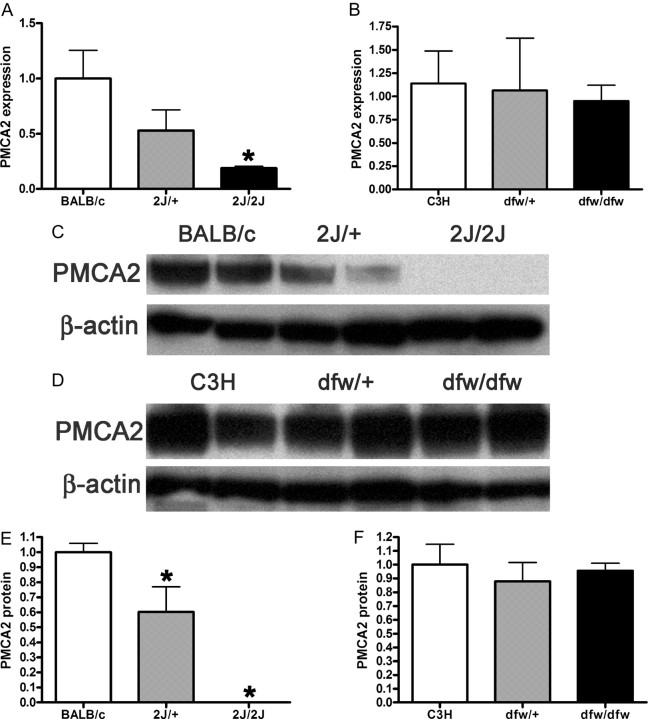
Fig. 3.
A, QRT-PCR demonstrates a progressive reduction in the expression of the PMCA2 gene (Atp2b2) in the mammary glands of dfw-2J/+ mice and dfw-2J/dfw-2J mice compared with wild-type BALB/c mice. PMCA2 mRNA levels were reduced by 50% in Dfw-2J/+ glands and by 85% in dfw-2J/dfw-2J glands. B, In contrast, PMCA2 mRNA levels in mice with the dfw mutation (dfw/+ and dfw/dfw) were not different from those in control C3H mice. C, Western blotting for PMCA2 in the plasma membrane fraction of lactating mouse mammary glands revealed abundant PMCA2 in BALB/c mice (lanes 1 and 2), reduced PMCA2 in dfw-2J/+ mice (lanes 3 and 4), and no PMCA2 in dfw-2J/dfw-2J mice (lanes 5 and 6). D, PMCA2 protein levels were similar in C3H (lanes 1 and 2), dfw/+ (lanes 3 and 4), and dfw/dfw (lanes 5 and 6) mice. E and F, Quantitation of PMCA2 protein normalized to β-actin protein levels in blots from C and D. Protein levels generally paralleled mRNA levels, with the exception that PMCA2 mRNA was detectable in dfw-2J/dfw-2J mice, but PMCA2 protein was not. An asterisk denotes statistical significance.