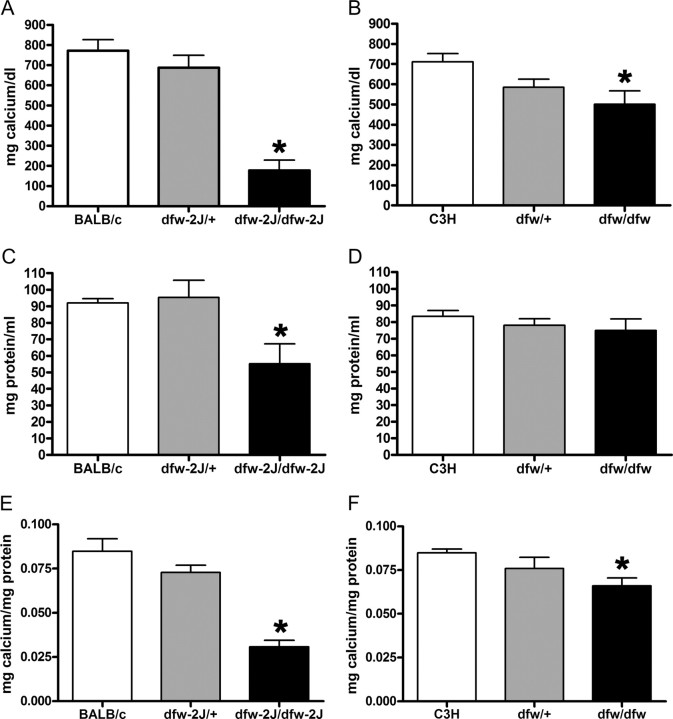
Fig. 4.
Milk calcium concentrations are reduced in PMCA2 mutant mice. A, On d 12 of lactation, milk calcium concentrations were approximately 70% lower (P < 0.01) in dfw-2J/dfw-2J mice (n = 4) than in BALB/c controls (n = 7). B, Milk from dfw/dfw mice (n = 4) had 30% less calcium (P < 0.05) than did milk from C3H controls (n = 5). In both cases, the heterozygous mice (dfw/+, n = 6; dfw-2J/+, n = 4) had milk calcium concentrations between the wild-type and homozygous mutant mice (A and B) but were not significantly different from wild-type mice. Milk protein levels (C and D) were also reduced in the dfw-2J/dfw-2J but not the dfw/dfw mutant mice (P < 0.01). Because most milk calcium is bound to proteins (mainly caseins), the milk calcium concentration was corrected for differences in protein content (E and F). Even when corrected for protein content, milk calcium levels were significantly reduced in dfw-2J/dfw-2J (P < 0.01) and dfw/dfw (P < 0.05) mutant mice. Statistical significance is represented with an asterisk.