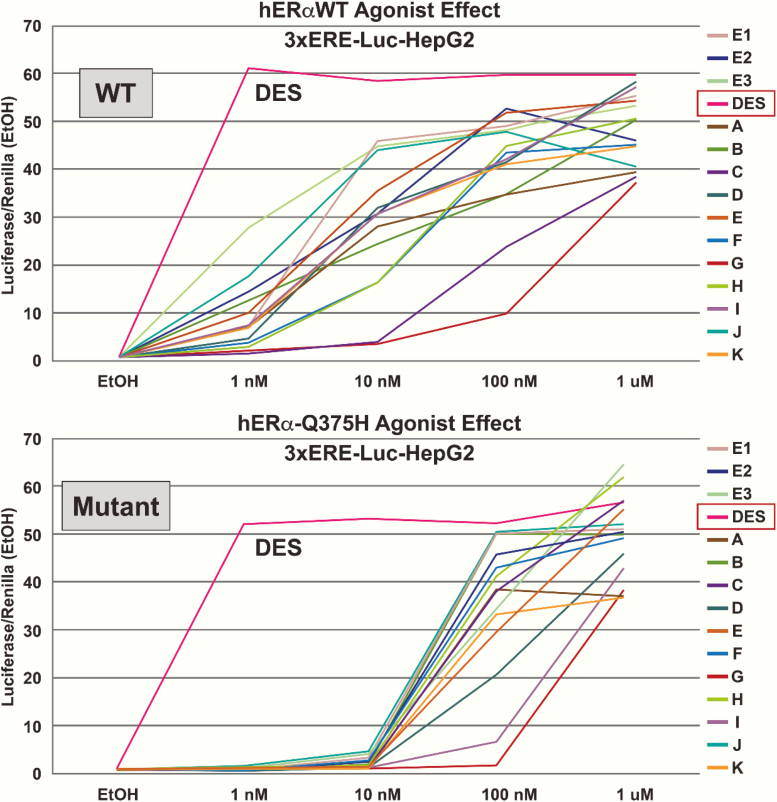
Figure 2.
Representative dose response reporter gene screen of a selection of compounds for estrogenic activity of the wild-type and Q-variant estrogen receptor (ER) in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HepG2) cells. DES was the most active compound tested compared with E2 and has a higher ligand-binding affinity to the wild-type ERα, surpassing the endogenous E2. Transactivation of the estrogen response element (ERE)-dependent–luciferase reporter gene in HepG2 cells resulted in a higher half maximal effective concentration (right-shifted), reflecting reduced estrogen signaling with the Q375H (variant). The data shown are the mean of the triplicate determinations in a representative experiment. (Values are presented as ± standard error of the mean [SEM]). Compounds tested: all 3 endogenous estrogen compounds: E1, estrone; E2, 17β estradiol; E3, estriol (not shown). Figure legend: [A] estrone; [B] D8,9-dehydroestrone; [C] equilin; [D] 17α-dihydroequilin; [E] 17β-dihydroequilin; [F] equilenin; [G] 17α-dihydroequilenin; [H] 17β-dihydroequilenin; [I] 17α-estradiol; [J] 17β-estradiol; [K] conjugated equine estrogen (mixed at the proprietary ratio for 10–2 M “estrogens”).