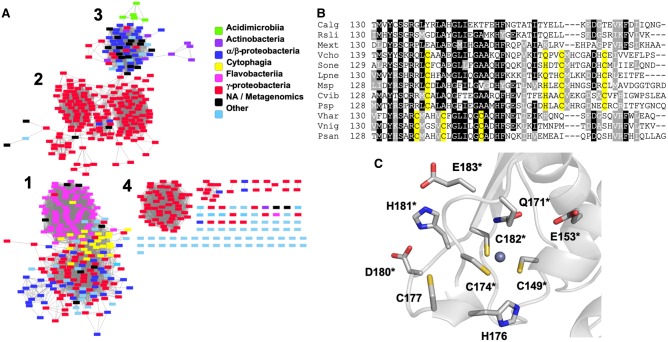
Figure 1. Conservation of zinc binding sites among H-NOX homologues.
(A) Sequence similarity network including 599 sequences filtered such that only edges associated with E-values less than 10−47 are included in the network. Sequences are represented by rectangles colored according to class. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of three representative sequences from each group in (A). Putative zinc-binding residues are highlighted in yellow. Species names are abbreviated as follows: (Group 1) Calg, Cellulophaga algiola; Rsli, Runella slithyformis; Mext, Methylobacterium extorquans; (Group 2) Vcho, Vibrio cholerae; Sone, Shewanella oneidensis; Lpne, Legionella pneumophila; (Group 3) Msp, Mycobacterium sp.; Cvib, Caulobacter vibrioides; Psp, Pseudomonas sp. DY-1; (Group 4) Vhar, Vibrio harveyi; Vnig, Vibrio nigripulchritudo; Psan, Photobacterium sanguinicancri. (C) Zinc coordination environment in a Vc H-NOX homology model. Each of the residues in the figure has been mutated to Ala and those indicated by asterisks result in insoluble protein.