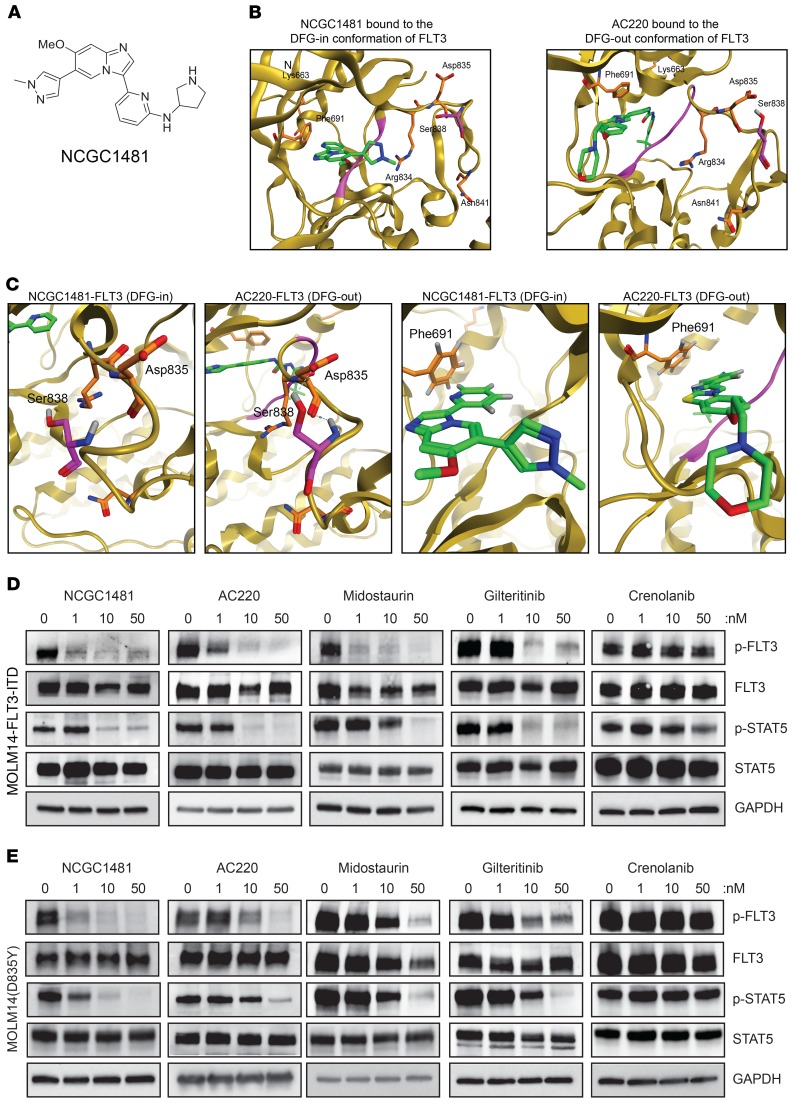
Figure 1. Chemical structure and inhibitory function of NCGC1481.
(A) Chemical structure of NCGC1481. (B) A ribbon/surface representation of the cocrystal of NCGC1481-FLT3 (PDB: 6IL3) and a ribbon/surface representation of the cocrystal of AC220-FLT3 (PDB: 4XUF). (C) Detailed view of the Asp835-Ser838 hydrogen bond formed in the cocrystal of NCGC1481-FLT3 relative to loss of this hydrogen bond in the cocrystal of AC220-FLT3 (left 2 panels). Detailed view of the F691-ligand hydrogen bond formed in the cocrystal of NCGC1481-FLT3 and the cocrystal of AC220-FLT3 (right 2 panels). (D) Immunoblotting of isogenic MOLM14-FLT3-ITD cell lines treated with the indicated inhibitors for 90 minutes. (E) Immmunoblotting of MOLM14-FLT3-ITD(D835Y) cell lines treated with the indicated inhibitors for 90 minutes. See complete unedited blots in the supplemental material.