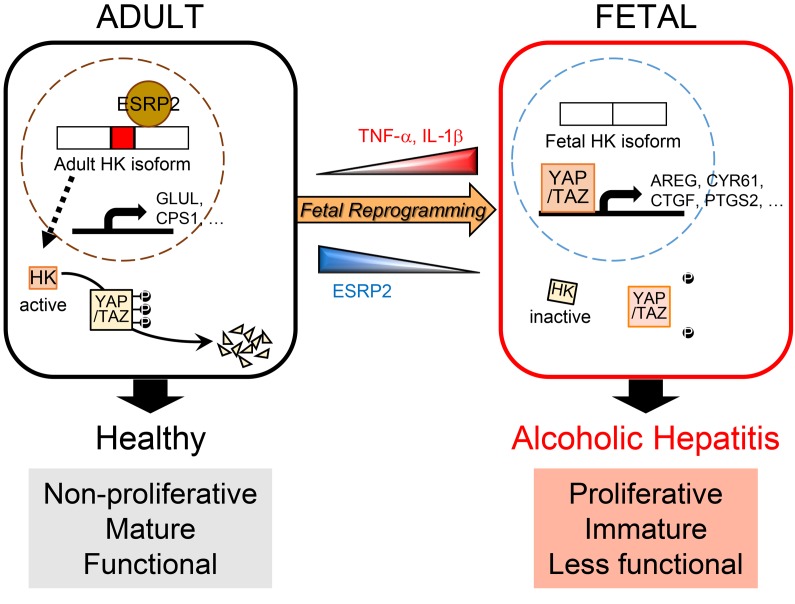
Figure 10. Model for liver failure in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis (SAH).
Inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, suppress ESRP2, an adult RNA-splicing factor. Loss of ESRP2 permits fetal RNA-splicing variants of HKs to accumulate. Because fetal HKs are relatively inactive, phosphorylation and clearance of their targets, YAP/TAZ, are impaired, allowing these fetal transcription factors to accumulate and reactivate fetal gene expression programs. Thus, the surviving adult hepatocytes are reprogrammed to become more fetal like and regenerative, but less mature. This provokes loss of critical adult hepatocyte functions, including ammonia detoxification and clotting factor biosynthesis, and causes the clinical features of liver failure.