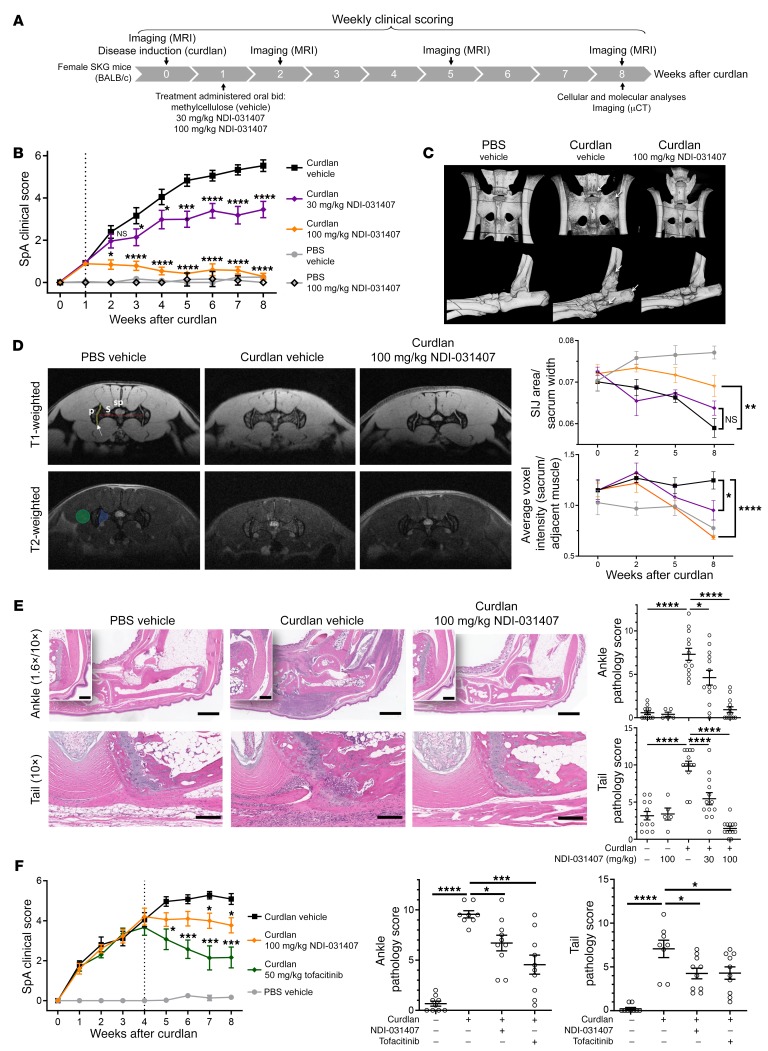
Figure 2. TYK2 inhibition by small molecule prevents SpA disease progression in SKG mice.
Female SKG mice were treated with curdlan to induce SpA-like disease, or with PBS as disease-free controls. (A) Overview of experiment and readouts for B–E. At 1 week after curdlan treatment, mice began treatment with NDI-031407 at the indicated dosages by gavage twice daily. (B) Mice (n = 12–13 per group) were scored weekly for SpA symptoms (blepharitis, arthritis, and dermatitis). (C) Representative postmortem μCT images of pelvis (dorsal view) and ankles (lateral view) from mice in the indicated groups. Arrows point to sites of entheseal erosion. (D) MRI of the sacroiliac joint (SIJ; coronal plane) in live mice. T1 weighing was used to assess SIJ area as a ratio to sacrum width. SP, spinal cord; S, sacrum; P, pelvis; red line, sacrum width; yellow area/white arrow, SIJ space. Scale bar: 5 mm. T2 weighing was used to assess bone marrow edema in the sacrum (blue area) normalized to adjacent muscle (green area). Representative images at 8 weeks after disease induction. Pooled data from 5 mice per group. Group colors are the same as in B. (E) H&E staining and scoring of tissue at 8 weeks after curdlan. Scale bars: 1 mm for 1.6× and 200 μm for 10×. (F) SKG mice were treated from 4 weeks after curdlan (therapeutically) with NDI-031407 or tofacitinib for 4 weeks (n = 9–10 per group). Data in B, D, and F were assessed by 2-way ANOVA, with time considered as dependent variable. Means of curdlan/NDI-031407–treated animals compared with curdlan/vehicle-treated controls at each time point by Dunnett’s post hoc test. For pathology scoring (E and F), each point represents a single mouse; disease-free vs. curdlan/vehicle animals were analyzed by unpaired t test, NDI-031407–treated vs. vehicle-treated animals by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.