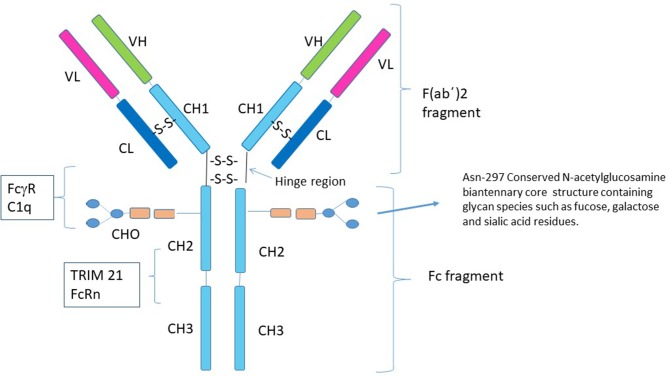
Figure 1.
Structure of IgG1. Human IgG consists of four subclasses (IgG1–IgG4) that differ in the number of disulfide bonds in the hinge region, amino acid residues throughout the constant chain as well as their glycosylation patterns. Although the conserved N-linked glycosylation site at Asn-297 is necessary for stabilization of the Fc fragment and its removal abolishes Fc effector functions of IgG (7–9), it is not absolutely required for the anti-inflammatory activity of Fc multimers. Residues near the lower hinge region, CH2 and CH3 are involved in binding to FcγRs and C1q. The FcRn and TRIM21 bind to residues within both the CH2 and CH3 region. The majority of studies with recombinant Fc proteins for use as replacement IVIG have focused on introducing sequences that allow for aggregation of the recombinant Fc molecules, for example addition of a IgG2 hinge region as a multimerization domain to the IgG1 Fc (10, 11).