Figure 1.
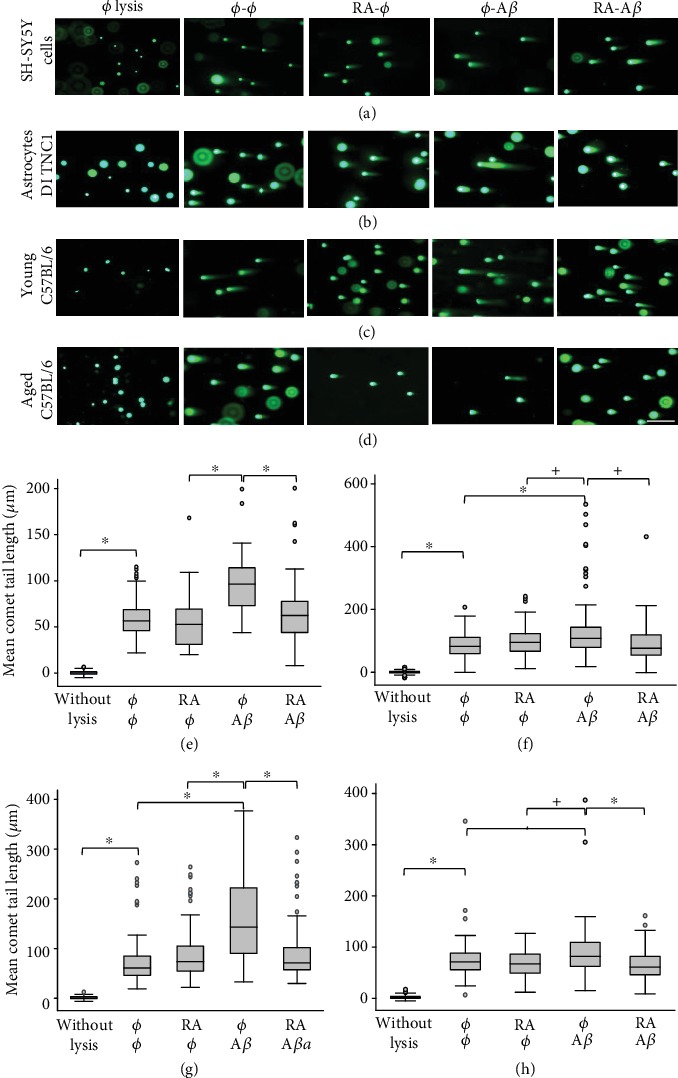
All-trans-retinoic acid (RA) protects against Aβ-induced DSBs in SH-SY5Y and astrocytic DI TNC1 cells as well as in the neocortex of young and aged male C57BL/6J mice. Representative pictures of comets with various tail lengths of (a) SH-SY5Y cells, of (b) DI TNC1 cells, and of cortical tissues originating from (c) young (4 months; n = 3 mice) or (d) aged (16 months; n = 3) mice following RA (5 μM) and/or Aβ (20 μM) in vitro treatments for 2 × 30 min (SH-SY5Y cells; cortical tissue) and 2 × 1 h (DI TNC1 cells). ø = without treatment; scale bar: 200 μM. Box plots of mean comet tail lengths of (e) SH-SY5Y cells (number of cells measured: 33 < n < 52), of (f) DI TNC1 cells (55 < n < 72), of (g) 3 young (30 < n < 55), and of (h) 3 aged mice (31 < n < 57). ANOVA with Bonferroni correction: one experiment for SH-SY5Y cells (replicated in Figure 4(e)) and 3 for DI TNC1 cells; ∗p < 0.05 for all experiments or all three mice; +p < 0.05 for 2 out of 3 mice; ◊p < 0.05 for 1 out of 3 mice.
