Figure 3.
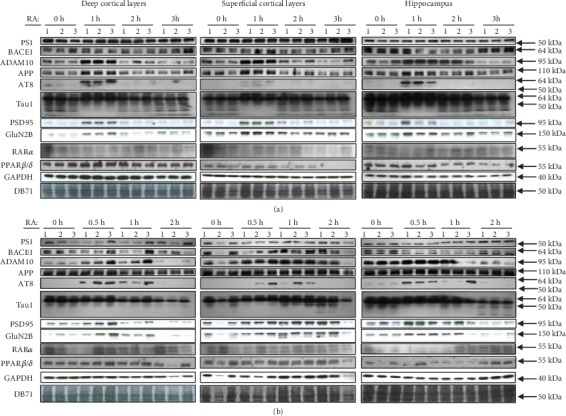
Changes in protein expression following 1 μM all-trans-retinoic acid (RA) treatment of the deep and superficial neocortical layers, as well as of the hippocampus, of (a) three 1-month-old and (b) three 17-month-old male C57BL/6J mice. The proteins are involved in the amyloid cascade (Presenilin 1 or PS1/γ-secretase, BACE1/β-secretase, ADAM10/α-secretase, and APP C-terminus), in Tau phosphorylation (phospho-Tau (AT8) or unphosphorylated Tau (Tau1)), in synaptic functions (PSD95, GluN2B/NR2B), or in RA-dependent pathways (RARα, PPARβ/δ). GAPDH and DB71 stainings were used to demonstrate equal loading of the Western blot gels. Overall, we observed significant increases (see Section 3.3) of ADAM10, APP, and phosphorylated and unphosphorylated Tau proteins, suggesting the activation of neuroprotective mechanisms following the RA treatment, whereas the expression of the enzymes of the amyloidogenic pathway, PS1 and BACE1, or, in most cases, of the RA receptors was not increased. Protein sizes are indicated on the right. A size range is given for Tau isoforms (AT8 and Tau1).
