Figure 6.
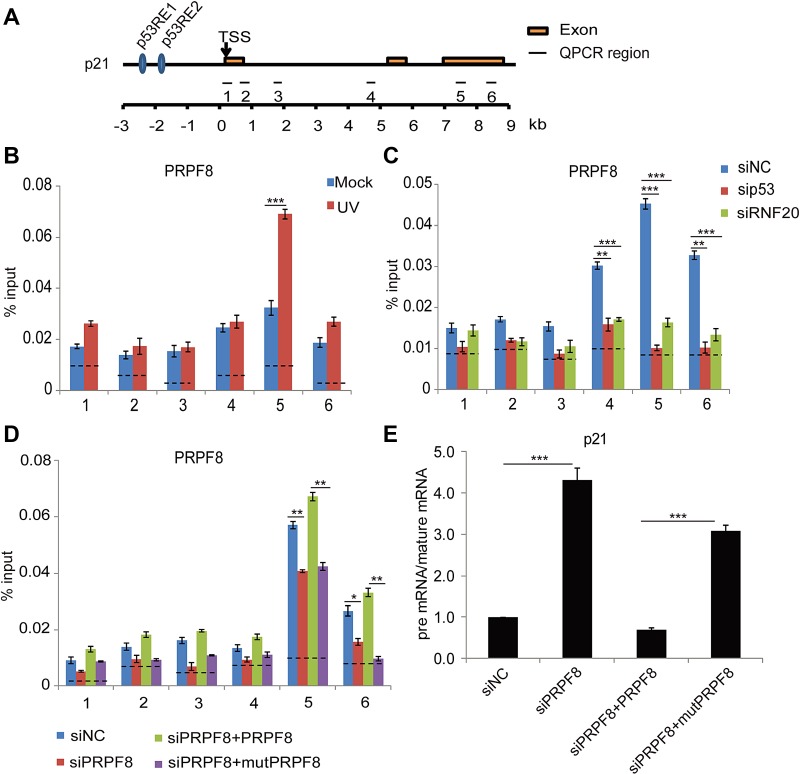
ubH2B mediates the recruitment of PRPF8 for pre-mRNA processing of p21. (A) Schematic representation of p21 genomic locus. p53 RE1, p53 response element 1; p53 RE2, p53 response element 2; TSS, transcription start site. (B) PRPF8 is recruited to the gene body of p21 upon DNA damage. HCT116 cells were treated with or without UV-C (20 J/m2). After 8 h recovery, ChIP analyses at the p21 locus were performed using anti-PRPF8 antibody. An irrelevant IgG was used for negative control presented as the dotted lines. Primer pairs used for quantitative PCR following ChIP are indicated in schematic diagram. The primer sequences have been included in Supplementary Table S3. (C) Downregulation of p53 or the RNF20/40 complex by siRNA impairs the enrichment of PRPF8 at the gene body region of p21. HCT116 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA followed by UV-C (20 J/m2). After 8 h recovery, ChIP analyses at the p21 locus were performed using anti-PRPF8 antibody. (D) The C-terminal ub-binding mutant of PRPF8 (mutPRPF8) impairs the enrichment of PRPF8 at the gene body region of p21. Wild-type PRPF8 or the I2105A/I2106A mutant (mutPRPF8) was expressed in the siRNA knockdown cells. The ChIP assays were performed using anti-PRPF8 antibodies in response to UV-C (20 J/m2). (E) MutPRPF8 impairs the pre-mRNA processing of p21. HCT116 cells were treated with indicated siRNA. Full-length PRPF8 or the I2105A/I2106A mutant was re-introduced into the cells. The cells were irradiated with UV-C (20 J/m2). The relative changes of pre-mRNA vs. mature mRNA of p21 were examined by quantitative PCR. The sequences of each primer are shown in Supplementary Table S5. Data are represented as mean ± SD as indicated from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
