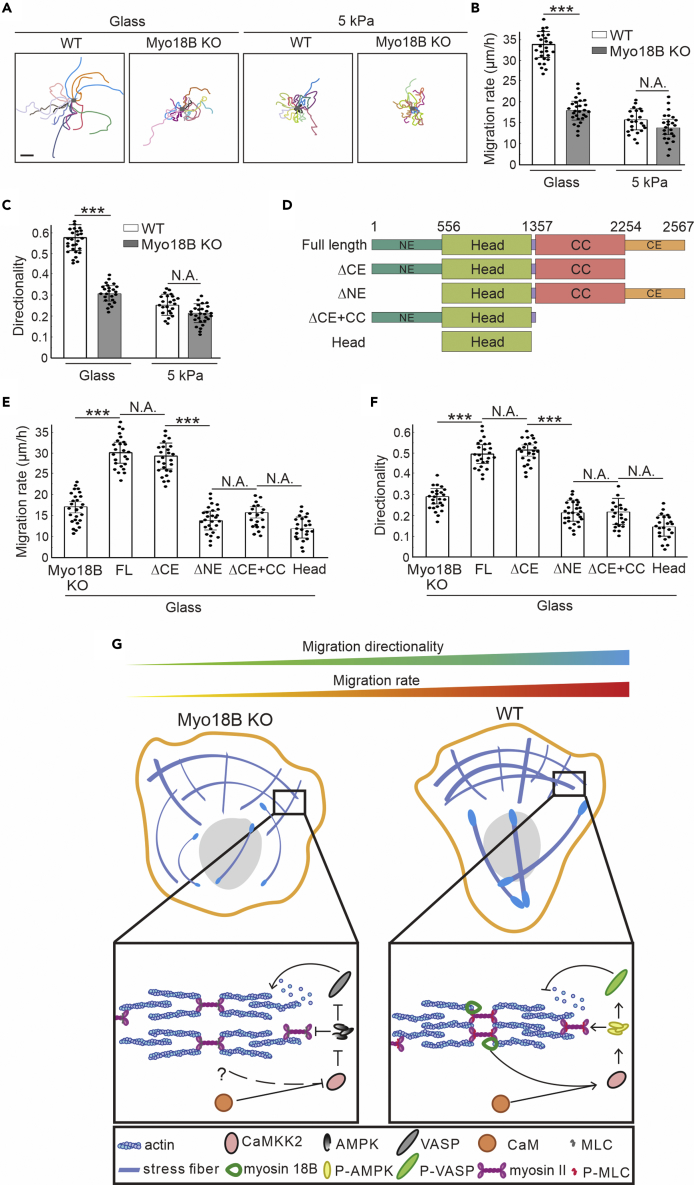
Figure 4.
Myosin-18B Deletion Inhibits the Directed Migration of Cells on Rigid Substrates
(A) Representative images of the moving trajectory of individual wild-type or myosin-18B knockout cell seeded on fibronectin-coated glass or 5-kPa matrix. Scale bar, 40 μm.
(B and C) Quantification of the (B) migration rate and (C) directionality of wild-type (n = 27 for glass, n = 23 for 5 kPa) and myosin-18B knockout cells (n = 24 for glass, n = 28 for 5 kPa).
(D) Truncated myosin-18B constructs used in the rescue experiments.
(E and F) Quantification of the (E) migration rate and (F) directionality of different myosin-18B constructs expressed in myosin-18B knockout cells. n = 25 for myosin-18B-FL-GFP, n = 25 for ΔCE-myosin-18B, n = 27 for ΔNE-myosin-18B, n = 21 for ΔCE + CC-myosin-18B, and n = 23 for head-myosin-18B transfected cells were used for quantification. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student's t test).
(G) A working model for the regulation of myosin-18B in the mechanosensitive CaMKK2-AMPK-VASP/MLC signaling cascade and directed cell migration.