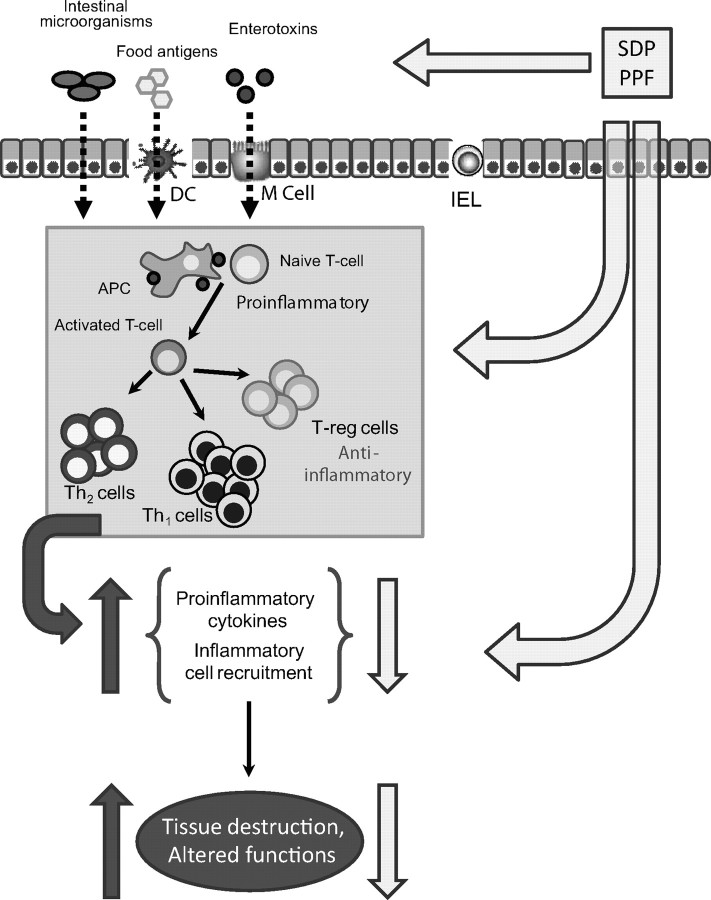
Figure 7.
Diagram summarizing the mode of action of plasma supplements [spray-dried plasma, (SDP) or plasma protein fraction (PPF)]. Food proteins and products from commensal bacteria can be taken up by M cells present in Peyer's patches, by dendritic cells (DC) of the lamina propria, or by transcytosis (especially at early stages of development). Antigens are then presented to naive CD4 T cells and activated. Activated lymphocytes produce proinflammatory cytokines that amplify the immune response and induce inflammatory cell recruitment. In an inflammatory state, immune cells release reactive oxygen species (ROS) to eliminate invaded pathogens; however, these agents also induced gut alterations and tissue destruction. Plasma protein supplementation can modulate the immune response at luminal level (e.g., modifying the microbiota profile, pathogen binding); biologically active compounds present in plasma supplements can also interact directly with mucosal immune cells. The plasma-induced changes in mucosal cytokine profile will prevent or reverse deleterious effects resulting from immune system activation. IEL = intraepithelial lymphocytes; T-reg = regulator T-lymphocytes; APC = antigen presenting cells; Th1 = T helper type 1; Th2 = T helper type 2.