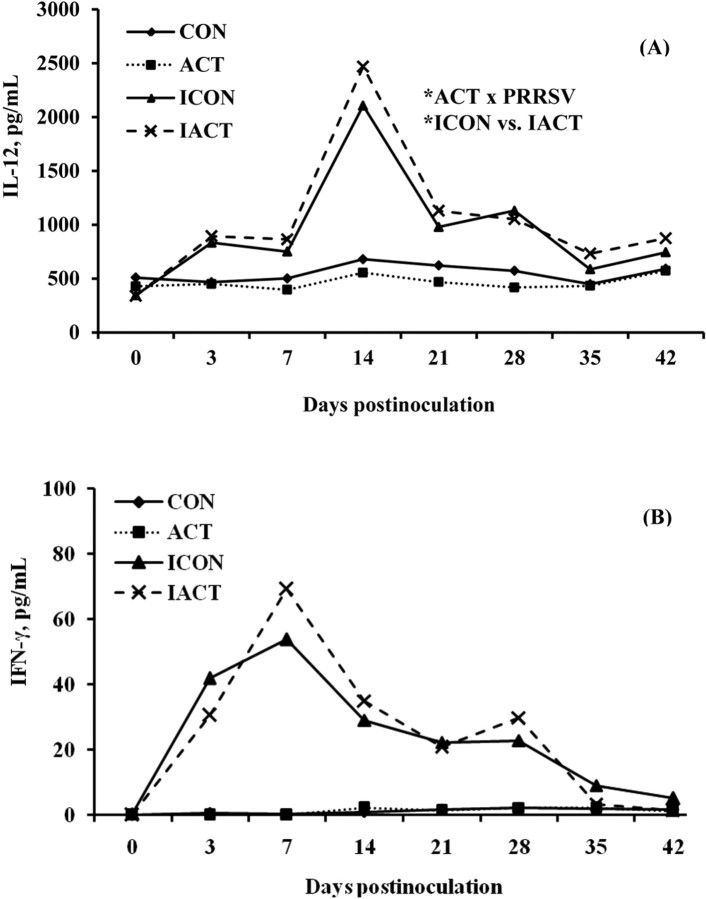
Figure 4.
(A) Serum IL-12 and (B) interferon (IFN)-γ concentrations in pigs fed control or mannan oligosaccharide (Actigen; ACT, Alltech, Inc., Nicholasville, KY) diets with or without porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) infection. The IFN-γ and IL-12 concentrations of infected pigs were greater than those of uninfected ones (P < 0.001). There were no effects of diet on either cytokine. There was an ACT × PRRSV interaction (P = 0.026) for IL-12 only, indicating that infected pigs fed ACT had a greater concentration of IL-12 than those fed the control (P = 0.048). There were also significant effects of day or interaction of day x PRRSV on IFN-γ and IL-12 (P < 0.001). Values were means; pooled SEM were 33.4 and 1.6 pg/mL for IL-12 and IFN-γ, respectively. A pig was an experimental unit; each treatment had 8 pigs except ICON (7 pigs, 1 pig euthanized at 18 d postinfection). CON: uninfected control-fed pigs; ACT: uninfected ACT-fed pigs; ICON: infected control-fed pigs; IACT: infected ACT-fed pigs. *P < 0.05.