-
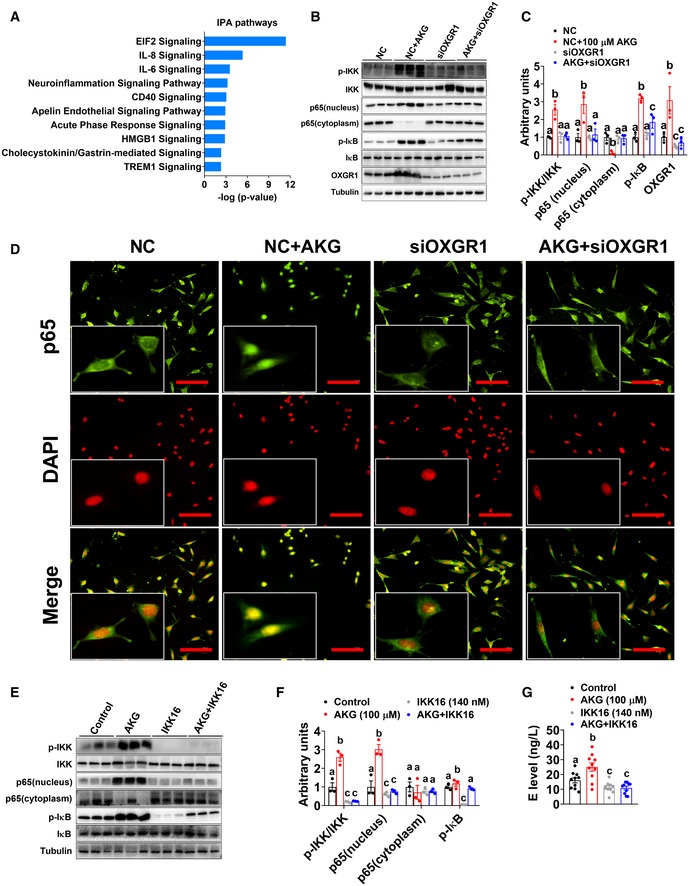
A
Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) of AKG‐induced transcriptome signature in adrenal chromaffin cells treated with AKG. The mRNA was extracted from adrenal chromaffin cells after 3‐h incubation of vehicle or AKG (100 μM) (n = 3 per group).
-
B, C
Immunoblots (B) and quantification (C) of p‐IKK/IKK, p65, p‐IκB/IκB, and OXGR1 protein in adrenal chromaffin cells cultured with vehicle + NC, vehicle + siOXGR1, AKG (100 μM) + NC, or AKG + siOXGR1 for 3 h (n = 3 per group).
-
D
p65 translocation in adrenal chromaffin cells cultured with vehicle + NC, vehicle + siOXGR1, AKG (100 μM) + NC, or AKG + siOXGR1 for 3 h (n = 3 per group). Scale bars, 100 μm.
-
E, F
Immunoblots (E) and quantification (F) of p‐IKK/IKK, p65, and p‐IκB/IκB protein in adrenal chromaffin cells cultured with vehicle, AKG (100 μM), IKK inhibitor IKK16, or AKG + IKK16 for 3 h.
-
G
E level in the medium from adrenal chromaffin cells cultured with vehicle, AKG (100 μM), IKK16, or AKG + IKK16 for 3 h (n = 10 per group).
Data information: Results are presented as mean ± SEM. In (C, F and G), different letters between bars indicate
≤ 0.05 by one‐way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's tests.