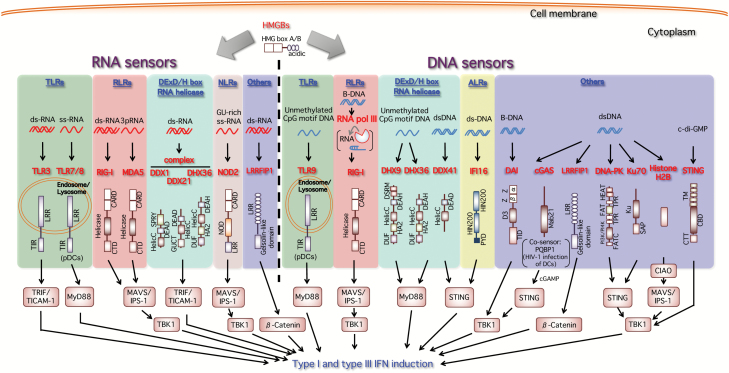
Fig. 1.
Nucleic acid sensors inducing type I and type III interferons. During viral infection, virus-derived nucleic acids (RNA and DNA) are mainly targeted by host nucleic acid sensors triggering the gene expression of type I and III interferons to induce anti-viral activities. As RNA sensors, TLR3 and TLR7/TLR8 sense viral RNAs on the endosomal or lysosomal membrane. RIG-I and MDA5 are ubiquitously expressed and recognize viral RNAs in the cytoplasmic space. Other RNA helicases DDX1, DDX21 and DHX36 form an RNA sensor complex in mDCs. The Nod-like receptor (NLR) NOD2 also detects the RSV-derived ssRNA genome to activate the MAVS/IPS-1 pathway. In the cases of DNA sensing, TLR9 detects DNA containing the unmethylated CpG motif. DAI (DLM-1/ZBP1) interacts with dsDNA and activates TBK1 and IRF-3 as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor. Cytoplasmic AT-rich dsDNA (B-DNA) is transcribed by host RNA polymerase III (RNA pol III) into 5′-triphosphate RNA (3pRNA), which becomes a RIG-I ligand. DHX36 and DHX9 intracellularly sense CpG class A and B, respectively, in mDCs. DNA-stimulated DDX41 and the ALR IFI16 interact with their adaptor protein STING. STING itself also serves as a sensor of CDNs such as bacterium-derived c-di-GMP as well as host-derived cGAMP generated by cGAS in response to microbe- and host-derived cytosolic DNAs. cGAS is a critical cytoplasmic sensor for the detection of both microbial and host DNAs. The cGAS–cGAMP–STING pathway is now recognized as a major intracellular dsDNA sensing pathway. DNA-PK, Ku70 and extrachromosomal histone H2B are also reported to function as cytosolic DNA sensors. As for Ku70, only type III interferon is induced. LRRFIP1 functions possibly as a cytosolic nucleic acid sensor that dually detects both RNA and DNA. HMGBs also bind to both double-stranded and single-stranded immunogenic RNAs and function as universal sensors for nucleic acid-mediated innate immune responses during viral infection.