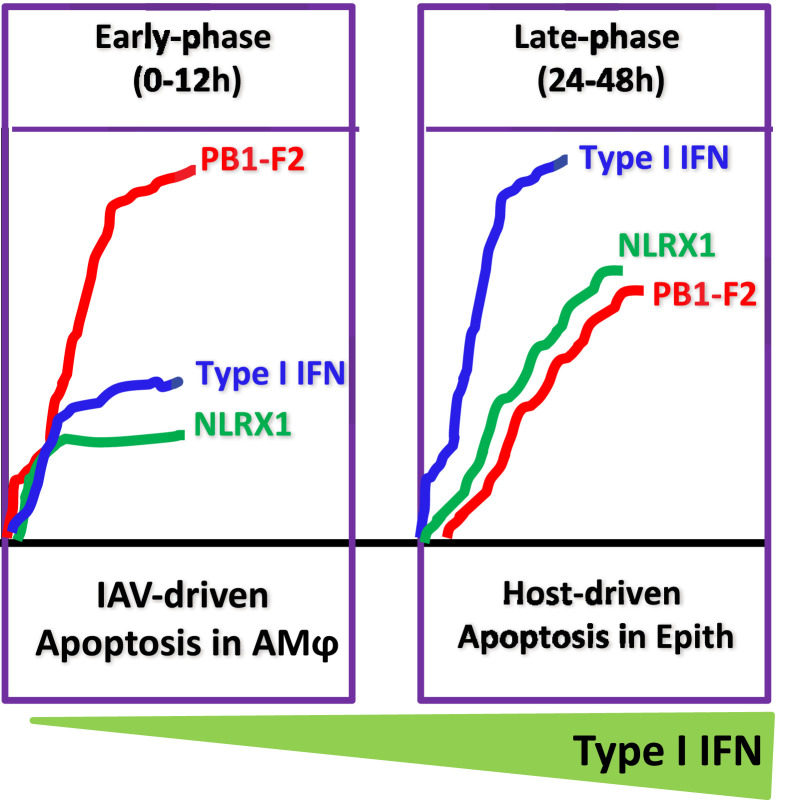
Fig. 2.
The impact of early versus late apoptosis of pulmonary macrophages on immunity to IAV infection. IAV induces early apoptosis in alveolar macrophages via the pro-apoptotic PB1-F2-IAV protein. We envision that the low levels of mitochondrial NLRX1 protein upon infection leads to early apoptosis and reduced production of type I IFN in alveolar macrophages. However, during the late phase of infection, high levels of mitochondrial NLRX1 protein disarm the pro-apoptotic function of PB1-F2 that leads to increased macrophage survival as well as IFN-I production. The increased levels of IFN-I in the alveolar space induce apoptosis in IAV-infected epithelial cells (Epith) and, thus, disrupt the niche for viral replication.