Fig. 2.
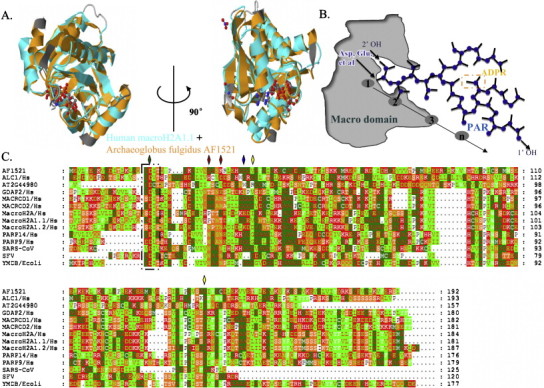
Macro domains are highly conserved structural domains that bind ADPR. (A) X-ray crystal structures of the macro domains from Archaeoglobus fulgidus (archaeal) Af1521 protein [18] (Protein Data Bank (PDB) accession code 2BFQ) and human macroH2A1.1 [22] bound to ADP-ribose (PDB accession code 3IID). The two views are rotated 90° relative to each other. (B) Schematic illustration of the proposed 2′ OH PAR capping function of macro domains, some amino-acids in conserved residues of macro domain proteins can serve as PAR acceptors, such as Asp, Glu. The square (orange) represents a mono-ADP-ribose. (C) Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of macro domain-containing proteins derived from SARS-CoV, SFV, Escherichia coli, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Archaeoglobus fulgidus with human macroH2A, MACROD1, MACROD2, GDAP2, PARP-9, PARP-14, and ALC1. The protein name is followed by the species abbreviation. Uniprot codes: AF1521 (Archaeoglobus fulgidus, O28751); AT2G44980 (Arabidopsis thaliana, Q3E6Q7); ymdB (Escherichia coli, C4ZRY6); ALC1 (human, Q86WJ1); GDAP2 (human, Q9NXN4); MACROD1 (human, Q9BQ69); MACROD2 (human, A1Z1Q3); PARP-9 (human, Q8IXQ6); PARP-14 (human, Q460N5); macroH2A1.1 and macroH2A1.2 (human, O75367); macroH2A (human, Q9P0M6). Conserved residues are colored according to their chemical properties. The black square represents the conserved motif (GDI/VT) among these different macro domain proteins. The bottle green diamond on top of the sequence indicates the amino acid that was mutated in AF1521 and ALC1, and red diamonds indicate the amino acids that were mutated in SARS-CoV. The blue diamond indicates the amino acid that was mutated in macroH2A1.1, and yellow diamonds indicate the amino acids that were mutated both in SFV and in MACROD1.
