Fig. 1.
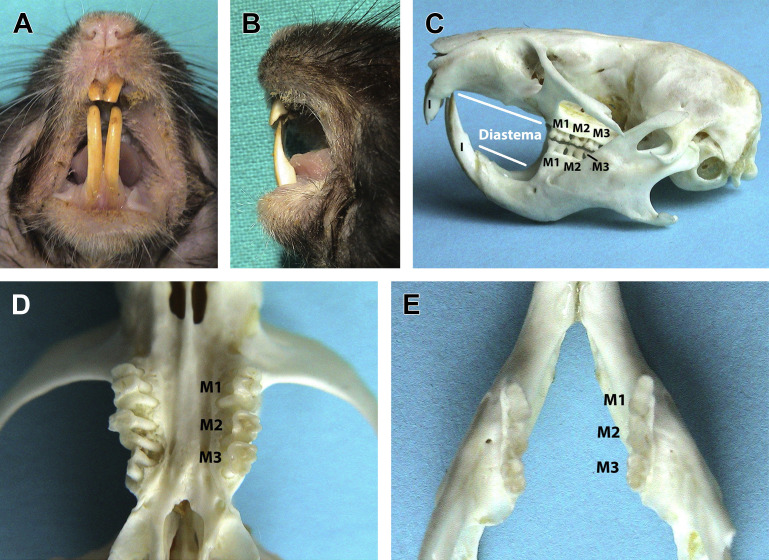
Dentition of the myomorph rodents shown in a golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus). (A) Labial aspect of the clinical crowns of incisor teeth. The enamel is yellow-orange. Divergence between mandibular incisors is variable due to the incomplete ossification and the flexibility of the mandibular symphysis. (B) Lateral (distal) aspect of incisor teeth. Clinical crowns are white because the enamel does not cover the distal, mesial, and lingual/palatal aspects of incisor teeth. Note the chisel-shaped occlusal plane and the enognathic appearance of the mandible. (C) Lateral view of the skull and jaws shown on a bony specimen displaying the long diastema and the anelodont, multiple rooted molar teeth. Unlike squirrel-like rodents, rat-like rodents lack premolar teeth. (D) Close up of the maxilla from the ventrodorsal view and (E) of the mandible from the dorsoventral view, displaying the molar teeth. Multiple roots are also visible in (D).
(Courtesy of Vittorio Capello, DVM, Milano, Italy; with permission.)