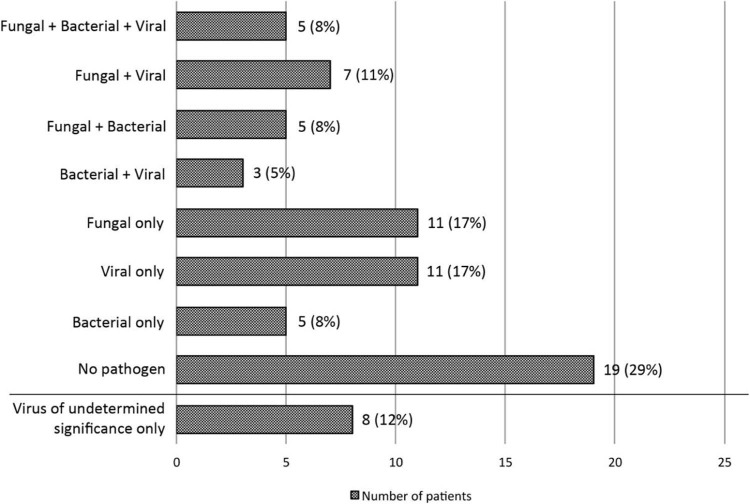
Figure 2.
Pathogen distribution among patients. Numbers of patients according to pathogen distribution are plotted against the horizontal axis. The following pathogens were observed in each group: Fungal + Bacterial + Viral: Talaromyces (n = 1), Aspergillus (n = 4), Stenotrophomonas (n = 3), Pseudomonas (n = 1), Escherichia coli (n = 1), CMV (n = 4), parainfluenza virus (n = 1); Fungal + Viral: Aspergillus (n = 4), Mucorales (n = 3), pneumocystis (n = 2), CMV (n = 5), influenza (n = 1), human metapneumovirus (n = 1); Fungal + Bacterial: Aspergillus (n = 4), Mucor (n = 1) pneumocystis (n = 1), Stenotrophomonas (n = 2), Klebsiella (n = 2), Pseudomonas (n = 1), Hemophilus influenzae (n = 1); Bacterial + Viral: CMV (n = 1), respiratory syncytial virus (n = 1), influenza (n = 1), Pseudomonas (n = 1), Enterobacter (n = 1), Legionella (n = 1); Fungal only: Aspergillus (n = 8), Mucorales (n = 3), pneumocystis, (n = 2); Viral only: CMV (n = 9), respiratory syncytial virus (n = 1), influenza (n = 1); Bacterial only: E. coli (n = 2), Staphylococcus aureus (n = 1), Klebsiella (n = 1), Pseudomonas (n = 1); Virus of uncertain lung pathogenicity: AdV (n = 4), HHV-6 (n = 3), HRV (n = 2), human bocavirus (n = 2), varicella zoster virus (n = 1), herpes simplex virus type 1 (n = 1). Only pathogen findings with established pathogenicity as outlined in Methods section were included in the first 7 groups.