Fig. 2.
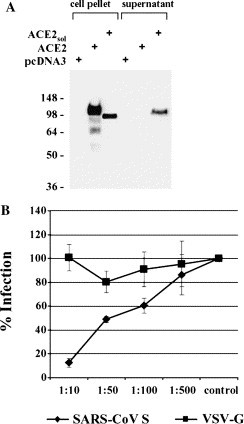
Expression of soluble ACE2 protein and inhibition of SARS-CoV S-driven infection. (A) Expression of the soluble ACE2 ectodomain. Either a pcDNA3 control vector (lane 1), wild type ACE2 (lane 2) or an ACE2 variant comprising only the ectodomain (lane 3) was transiently expressed in 293T cells. After 48 h, cells and culture supernatants (lanes 4–6) were harvested and analyzed for ACE2 expression via Western blot. (B) Inhibition of S-mediated entry into 293T cells by soluble ACE2. S-bearing pseudotypes and VSV-G pseudotypes normalized for equal luciferase activity (104 c.p.s.) upon infection of target cells were pre-incubated with the indicated dilutions of concentrated soluble ACE2 and used for infection of 293T cells. Luciferase activity was determined in cell extracts after 72 h. The relative luciferase units obtained after infection in the absence of soluble ACE2 was set as 100%. Each experiment was performed in quadruplicate and repeated three times; similar results were obtained with a different soluble ACE2 preparation and with independent virus stocks.
