Figure 5.
LTβR-Dependent FRC Maturation
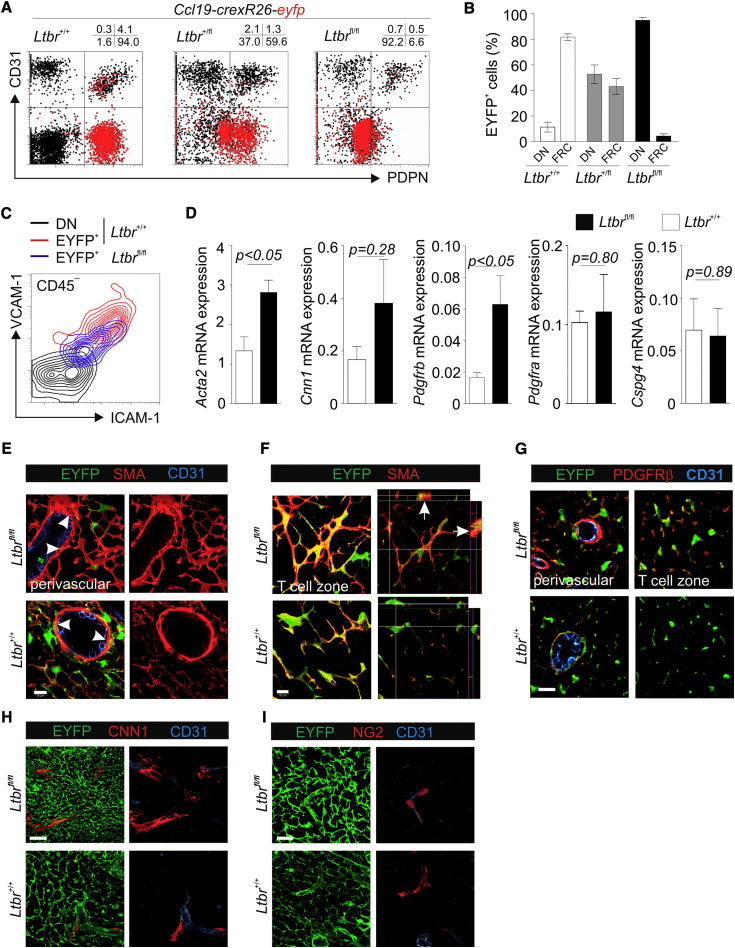
(A) LN stromal cells from 6-week-old Ccl19-cre × R26-eyfp mice with wild-type (+/+, WT) and heterozygously (+/fl) or homozygously floxed (fl/fl) Ltbr loci were assessed by flow cytometry for EYFP expression by using back gating. Representative dot plot analysis with quadstat values of CD31 and PDPN expression is shown.
(B) EYFP expression in FRCs and DN cells in the indicated Ltbr genotype of Ccl19-cre × R26-eyfp mice; mean ± SEM (n = 3 mice from two independent experiments).
(C) Representative analysis of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression on Ltbr+/+ DN cells from Ccl19-cre × R26-eyfp mice (black), EYFP+Ltbr+/+ FRCs of Ccl19-cre × R26-eyfp mice (red), and EYFP+ cells of Ccl19-cre × R26-eyfpxLtbrfl/fl mice (blue).
(D) Inguinal LNs from 6-week-old Ccl19-cre × Ltbrfl/fl and Ltbr+/+ controls were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR for the expression of Acta2 (SMA), Cnn1 (Calponin-1), Pdgfrb, Pdgfra, and Cspg4 (NG2). Values indicate mean ± SEM from two individual LNs from >3 mice analyzed in two independent experiments.
(E–I) Confocal microscopic analysis of inguinal LN stromal cells from 6-week-old Ccl19-cre × R26-eyfpxLtbrfl/fl mice and Ltbr+/+Ccl19-cre × R26-eyfp controls. Reconstruction of perivascular (E) and T cell zonal (F) stromal cell network by analyzing CD31, SMA, and EYFP expression is shown. Arrowheads indicate perivascular EYFP expression, arrows indicate SMA+EYFP+ cells in orthogonal sections, and scale bars represent 10 μm.
(G) Analysis of perivascular and T cell zonal expression of EYFP and PDGFRβ; scale bar represents 20 μm, all panels show merged channels. Reconstruction of perivascular and network-forming cells expressing CNN1 (H) and NG2 (I) and EYFP, merged channels in left panels; scale bars represent 30 μm; representative data out of three independent experiments. See also Figure S3.