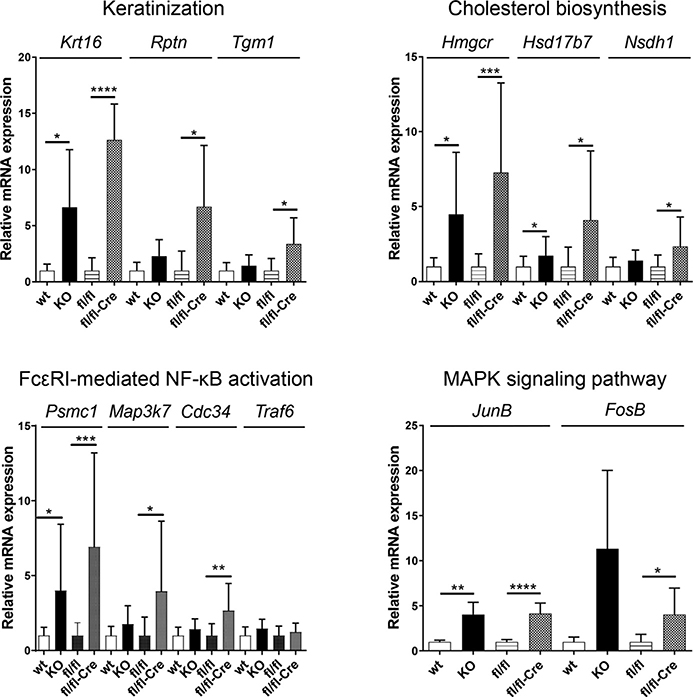
Figure 2. Increased expression of individual genes associated with keratinization, cholesterol biosynthesis, FcεRI-mediated NF-kB activation, and the MAPK pathway in the epidermis of neonatal Alox12b knockout mice and in adult mice upon tamoxifen-induced Alox12b inactivation.
Data were obtained by QRT-PCR from independent epidermis samples (wild-type, n = 5; Alox12b-KO, n = 5; fl/fl control, n = 8; fl/fl-Cre, n = 9). Means ± SD of fold inductions relative to the expression in wild-type epidermis and fl/fl control epidermis, respectively, are shown. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001. FcεRI, Fc epsilon receptor; fl/fl, control mice; fl/fl-Cre, Alox12bfl/fl/K14-CreJ mice; KO, knockout; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; QRT-PCR, quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase–PCR; SD, standard deviation.