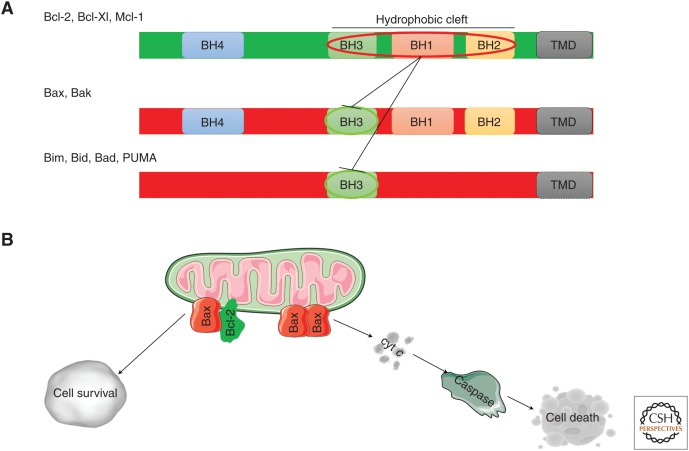
Figure 1.
Bcl-2 family of proteins. (A) Representation of the linear structure of the Bcl-2 proteins. The antiapoptotic (green) and the proapoptotic (red) family members are shown. The BH1-4 domains, the transmembrane domain (TMD), and the hydrophobic cleft are indicated. The sequestration of the BH3 domain of the proapoptotic proteins by the hydrophobic cleft of the antiapoptotic members, which mediates apoptosis prevention, is also indicated. (B) Bcl-2 proteins at the mitochondria. The antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins bind to the proapoptotic Bax/Bak proteins and BH3-only proteins, thereby neutralizing their proapoptotic activity and facilitating cell survival. Oligomerization of the proapoptotic Bax/Bak proteins in response to activator BH3-only proteins (such as Bim and truncated Bid) results in outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) permeabilization, enabling cytochrome c (cyt c) release into the cytosol with subsequent caspase 3/7 activation, eventually leading to cell death.