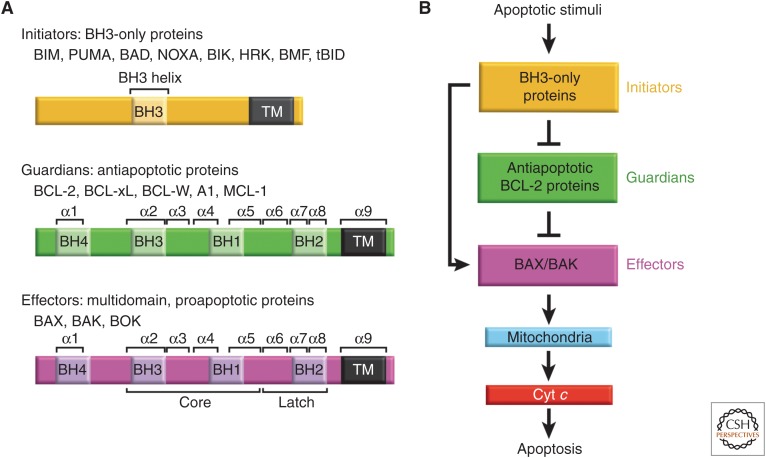
Figure 1.
The BCL-2 family and the intrinsic pathway to apoptosis. (A) Family members of the BCL-2 protein family. The family is made up of three subgroups of proteins related to each other by regions of sequence homology, the so-called Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains. Regions of secondary structure and domains discussed in the text are labeled. (B) BH3-only proteins, which generally only possess the BH3 domain, are up-regulated on apoptotic stimuli to initiate signaling of the pathway. BH3-only proteins interact with both the effectors BAX and BAK, and the antiapoptotic guardians. Guardians can protect against apoptosis by sequestering both the BH3-only proteins, thus inhibiting effector activation, and by neutralizing activated effector proteins directly. If freed, activated effectors oligomerize at the mitochondrial outer membrane leading to permeabilization of this barrier. This enables the release of apoptogenic factors into the cytosol, primarily cytochrome c (cyt c), leading to caspase activation and ensuing apoptosis. Emerging evidence indicates that BOK is a third member of the effector subgroup with alternative mechanisms of regulation (discussed later).