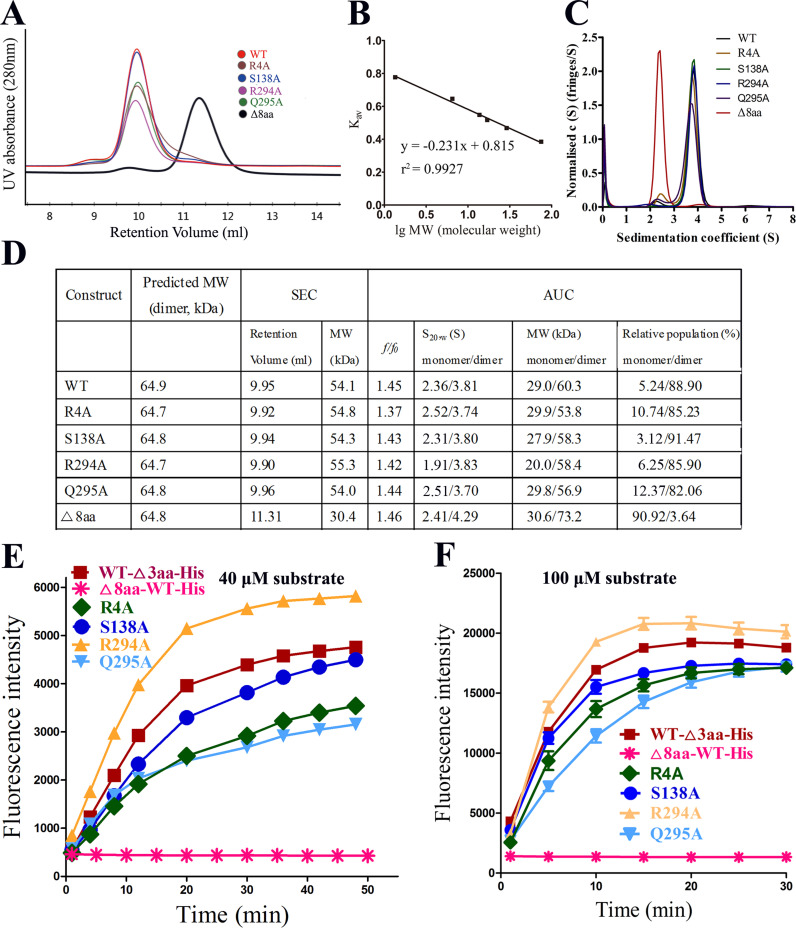
Fig. 4.
Mutational studies of several residues at the dimer interface. A. Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) analyses of the four site variants and the N-terminal-deletion variant (Δ8aa). WT, Δ8aa, Q295A, R294A, S138A and R4A are shown in red, black, orange, blue, yellow and green, respectively. B. Calibration curve. Conalbumin, 75 kDa; carbonic anhydrase, 29 kDa; equine myoglobin, 17 kDa; ribonuclease A, 13.7 kDa; aprotinin, 6.5 kDa; vitamin B12, 1.35 kDa (Bio-Rad and GE Healthcare) were used to calibrate the column. The values of the Y-axis were calculated using the equation Kav=(Ve−V0)/(Vt−V0). C. Sedimentation velocity analysis of the WT and variants. The major peak for each sample represents the major state of the protease. D. Calculated molecular masses based on the results of SEC and AUC assays, respectively. Δ8aa primarily exists as monomers. E. FRET-based mutational studies of the residues that may be involved in the dimerization of PEDV 3CLpro. The S138A, R4A, and Q295A variants exhibited reduced catalytic activity to various degrees (1, 0.74, 0.94, 1.22, 0.66, and 0.09, respectively; the activity of wild type PEDV 3CLpro was taken as 1). None of the three variants caused a great or complete loss of activity, and the catalytic activity of the R294A variant exhibited no reduction. Only the N-finger deletion variant exhibited a complete loss of activity. F. Same as that in panel E but with different substrate concentration.