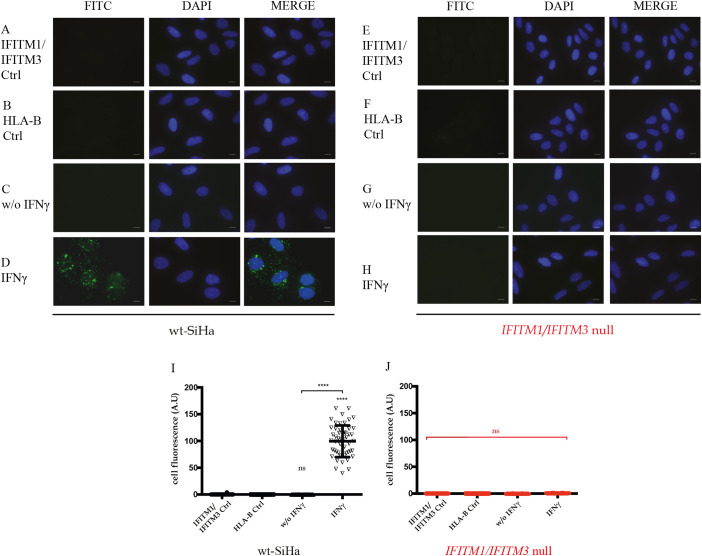
Fig. 7.
Evaluation of the IFITM1/IFITM3:HLA-B protein-protein interaction in situ. Proximity ligation assays were used to study the endogenous interaction between HLA-B and IFITM1/3 proteins in parental SiHa (A–D) and IFITM1/IFITM3 double null cells (E–H). Representative FITC images identify the protein-protein association foci (depicted in green) and DAPI was used for nuclear staining (depicted in blue). (A–B and E–F). Cells were incubated as negative controls using IFITM1/3 or HLA-B antibodies only. (C and G). Cells were incubated with both IFITM1/3 and HLA-B antibodies to define protein-protein foci in non-stimulated cells. (D and H) Cells were incubated with both IFITM1/3 and HLA-B antibodies to define protein-protein foci in IFN-γ stimulated cells. n = 3. Scale bar: 10 μm. (I and J) Quantification of HLA-B and IFITM1/3 total fluorescence per cell in presence or absence of IFNγ stimulation in (I) parental SiHa and (J) IFITM1/IFITM3 double null cells. For quantitation, three independent assays were performed, and each assay had two independent biological replicates. For each assay, fluorescence was measured in at least 50 cells per condition. Fluorescence was measured using ImageJ software. Statistical study was performed with 1-way Anova and Bonferroni correction (p-value < .0001). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)