Figure 2.
Structure of the Transmembrane Domain TMD of hNPC1
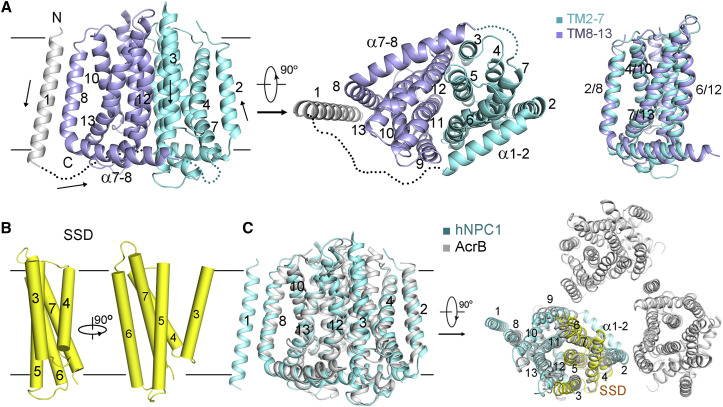
(A) TMs 2–13 of hNPC1 exhibit a characteristic resistance-nodulation-cell division superfamily fold. The two repeats in the RND fold are colored cyan and light purple, respectively. The invisible cytoplasmic segments are shown as dotted lines. The arrows in the left panel indicate the N→C orientation of the corresponding TMs. Right panel: TMs 2–7 are related to TMs 8–13 by a 180-degree rotation around an axis that is perpendicular to the membrane plane.
(B) The sterol sensing domain (SSD). TMs 3–7 of hNPC1 constitute the SSD that is also found in several proteins involved in sterol metabolism or signaling. Two perpendicular side views are shown.
(C) Structural similarity between the TMDs of hNPC1 and the bacterial multidrug efflux transporter AcrB. Right panel: the SSD-corresponding TMs in AcrB are exposed to the lipid bilayer in the context of trimer (PDB: 1IWG).