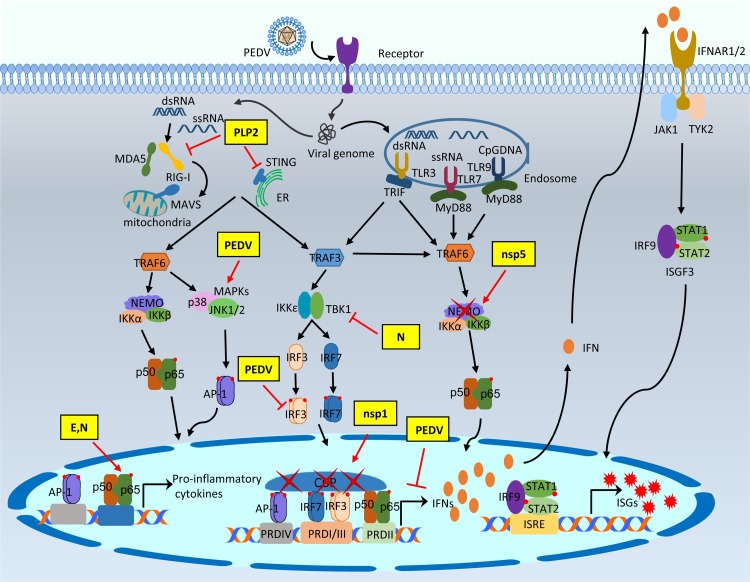
Fig. 3.
Modulation of type I IFN response by PEDV proteins. After binding to the celluar receptor APN, PEDV is internalized into target cells by direct fusion of viral-cellular membranes, and the viral genomic RNA is released into the cytosol for replication. The single-stranded viral RNA as well as dsRNA as a replicative intermediate are sensed by host innate nucleic acids sensors in the cytoplasm and the endosome. The activation of innate immune sensors further initiates the production of type I interferons or pro-inflammatory cytokines after binding of activated NF-κB, AP-1, IRF3, and IRF7 to the respective PRD regions. Type I IFNs are secreted and bind to the cell surface receptors of both virus-infected and non-infected neighbor cells to induce the nuclear localization of ISGF3 complex. Activation of JAK-STAT pathway induces the production of hundreds of interferon stimulating genes (ISGs) for establishment of the antiviral state. The PEDV IFN antagonists intervene the IFN signaling pathway at different stages. The modulation of the type I IFN response by PEDV and PEDV proteins are shown in yellow boxes.