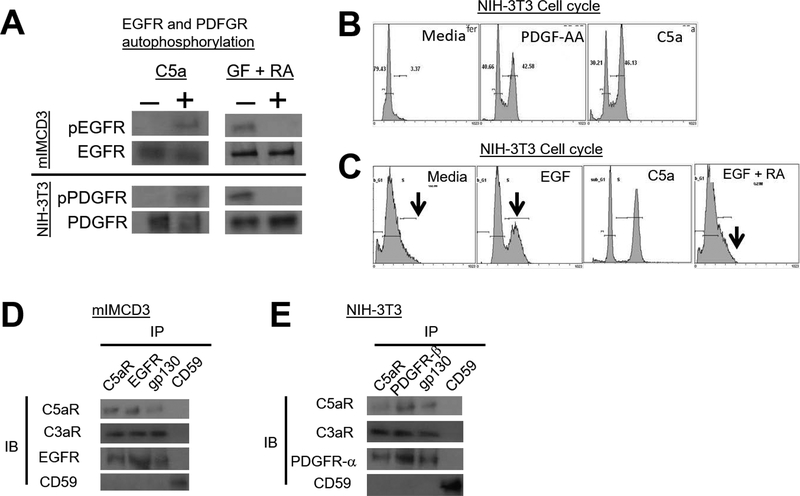
Figure 3. Autocrine C3ar1/C5ar1 signaling in non-immune cells is needed for PFGFR and EGFR autophosphorylation and cell cycle entry/progression.
(A) Upper: Serum-starved mIMCD3 (upper) or NIH-3T3 cells (lower) were incubated for 5 min with C5a (100 ng/ml) upper, or with GF (30 ng/ml) plus RA (10 ng/ml each) after which EGFR or PDGFR were IP’d and immunoblots of the IP’d EGFR and PDGFR probed for p-EGFR or p-PDGFR. (B) NIH-3T3 cells were incubated for 24 h with PDGF-AA (30 ng/ml) or C5a (100 ng/ml) and entry into cell cycles was assessed by propidium iodide incorporation. (C) Serum-starved NIH-3T3 cells were incubated for 24 h with EGF (30 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of RA (10 ng/ml each) and cell cycle entry was assessed by propidium iodide incorporation. (D) Serum-starved mIMCD3 and (E) serum-starved NIH-3T3 cells were incubated for 5 min with EGF (30 ng/ml) and PDGF-AA (30 ng/ml), respectively. Following detergent extraction of the cells with 1× Cell Lysis Buffer (10X) (Cell Signal, cat#9803) supplemented with 1mM PMSF and 1 Complete Mini protease inhibitor tablet (Roche Cat# 11836153001) and [1 mM Na Orthovanadate, anti-C5ar1, anti-EGFR, anti-PDGFR-α, anti-gp130, and anti-CD59 IPs were prepared. Immunoblots of the IP’d proteins were probed for C5ar1, C3ar1, EGFR, and CD59 and for C5ar1, C3ar1, PDGFR-α and CD59, respectively.