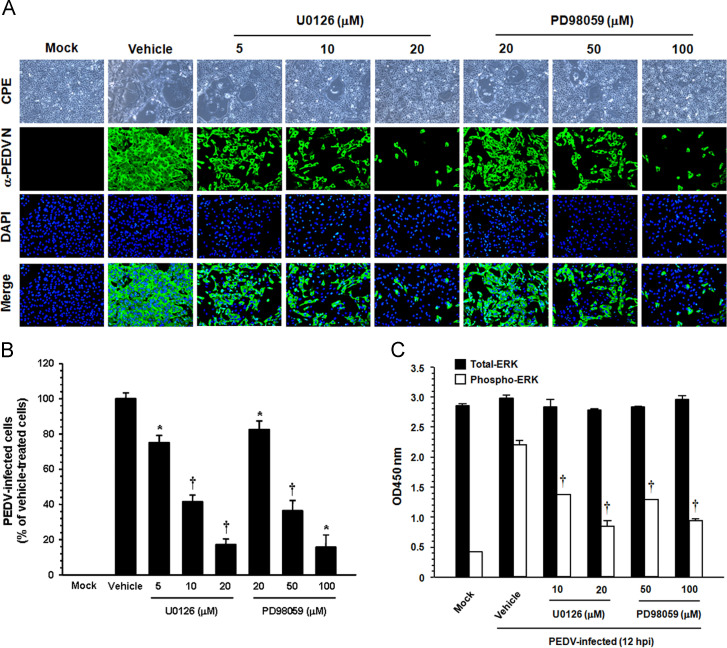
Fig. 4.
PEDV propagation is suppressed by inhibition of ERK1/2 activation. (A) Vero cells were preincubated with DMSO, U0126 (5, 10, and 20 μM), or PD98059 (20, 50, and 100 μM) for 1 h prior to infection and were mock-infected or infected with PEDV at an MOI of 1. Virus-infected cells were further maintained for 48 h in the presence of DMSO or inhibitors. PEDV-specific CPEs were observed daily and were photographed at 48 hpi using an inverted microscope at a magnification of 100× (first panels). For immunostaining, infected cells were fixed at 48 hpi and incubated with MAb against the N protein, followed by Alexa green-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody (second panels). The cells were then counterstained with DAPI (third panels) and examined using a fluorescent microscope at 200× magnification. (B) Viral production in the presence of each inhibitor was measured by quantifying the percentage of cells expressing N proteins through flow cytometry. Values shown are representative of three independent experiments and error bars represent standard deviations. (C) Chemical inhibition of ERK1/2 activation was quantitatively determined using FACE assay. Vero cells were mock-infected or PEDV-infected in the presence of DMSO, U0126 (10 and 20 μM), or PD98059 (50 and 100 μM). The cells were fixed at 12 hpi with 4% formaldehyde and incubated with an anti-ERK1/2 or anti-pERK1/2 antibody followed by HRP-conjugated IgG antibodies. The absorbance of the solution was determined at 450 nm using a spectrophotometer. These results represent the results of three independent experiments and error bars represent standard deviations. *, P=0.001 to 0.05; †, P<0.001.