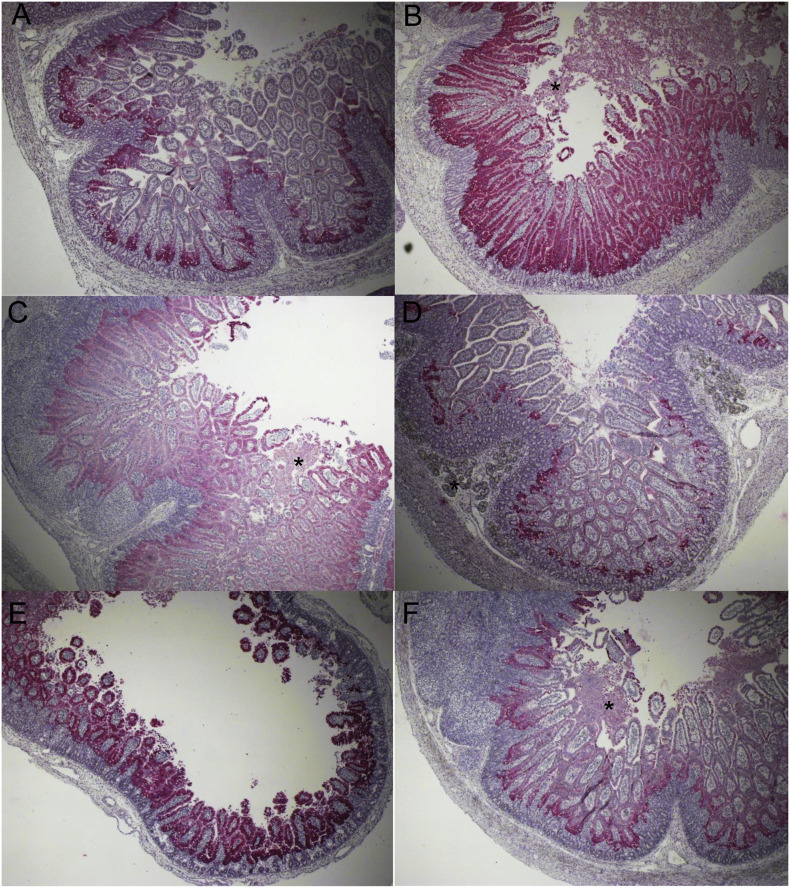
Fig. 2.
Immunohistochemical detection and distribution of PEDV antigen-positive cells in the duodenum, proximal jejunum, mid-jejunum, or ileum of gnotobiotic 9-day-old pigs inoculated with the original US PEDV strain PC21A. (A) Proximal jejunum of PEDV-inoculated pig 1 at post-inoculation hour (PIH) 16, showing low numbers of PEDV antigen-positive cells (red color) in the villus-crypt interface (B) Mid-jejunum of PEDV-inoculated pig 1 with no clinical signs (vomiting and diarrhea) at PIH 16, showing high numbers of PEDV antigen-positive cells (red color) in most of the villous epithelium. Note normal villous length and exfoliation of enterocytes on the villous tips (asterisk) (C) Ileum of PEDV-inoculated pig 1 at PIH 16, showing high numbers of PEDV antigen-positive cells (red color) in most of the villous epithelium. Note normal villous length and exfoliation of enterocytes on the villous tips (asterisk) (D) Duodenum of PEDV-inoculated pig 3 with vomiting (but no diarrhea) at PIH 16, showing low numbers of PEDV antigen-positive cells (red color) in the villus-crypt interface. Duodenal gland (asterisk) (E) Mid-jejunum of PEDV-inoculated pig 3 at PIH 16, showing high numbers of PEDV antigen-positive cells (red color) in most of the epithelium of atrophied villi (F) Ileum of PEDV-inoculated pig 3 at PIH 16, showing moderate numbers of PEDV antigen-positive cells (red color) in the villous epithelium. Note exfoliation of enterocytes on the villous tips (asterisk). Original magnification, all ×40. Fast Red, Gill's hematoxylin counterstaining. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)