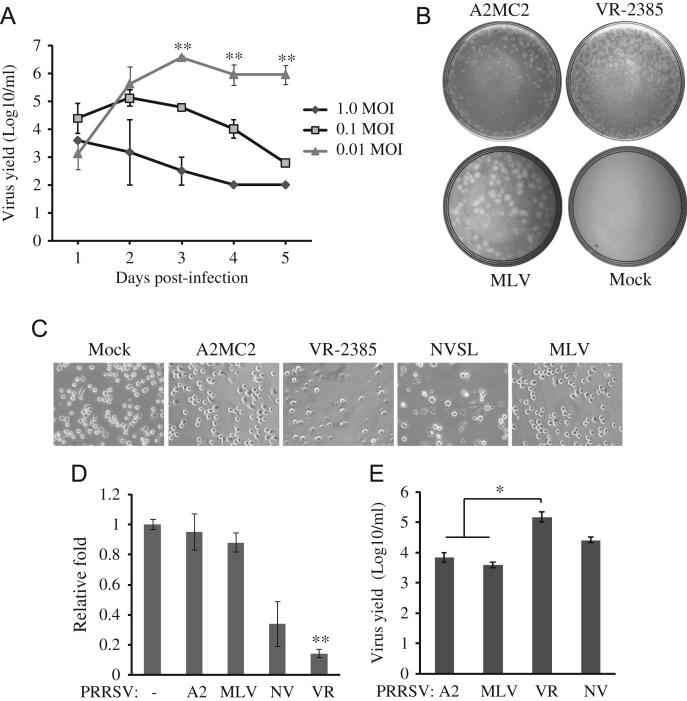
Fig. 3.
Growth properties of A2MC2 in MARC-145 and PAM cells. (A) Multi-step growth curve of A2MC2 in MARC-145 cells. The cells were inoculated with A2MC2 virus at a multiplicity of infection of 0.01, 0.1 or 1 TCID50 per cell. Virus yields at different time points after inoculation were titrated by an immunofluorescence assay. Error bars represent variation of three repeated experiments. Significant differences in virus yields between cells with 0.01 TCID50 and the rest two other groups are denoted by “**”, which indicate P-value of<0.01. (B) Plaque assay completed in MARC-145 cells. The cells were infected with diluted A2MC2, VR-2385 or MLV and overlaid with agarose. A plate of mock-infected cells was included as a negative control. Plaques were revealed at 4 dpi and photographed for comparison. (C) Cytopathic effect in PRRSV-infected PAMs. PAM cells were inoculated with PRRSV and at 20 hpi, observed using bright field microscopy. Mock-infected cells were included for comparison. PRRSV VR-2385 and NVSL led to cell death and lysis, while A2MC2 and MLV had little cytopathic effect. (D) Cell viability assay of PAMs. PRRSV-infected PAMs were assayed at 20 hpi with CellTiter-Glo kit (Promega). Relative fold cell viability in comparison with uninfected PAMs were plotted. Only VR-2385-infected cells had significantly lower viability (denoted by “**”, indicating P<0.01) viability than uninfected PAMs. A2: A2MC2, NV: NVSL, VR: VR-2385. (E) Virus yield titrated using MARC-145 cells. Cell culture supernatant samples from PRRSV-infected PAMs at 24 hpi were titrated in MARC-145 cells by IFA. Median tissue culture infectious dose per ml is shown. Error bars represent variation of three repeated experiments. The virus yields of A2MC2 and MLV were significantly lower (denoted by “*”, indicating P<0.05) than VR-2385.