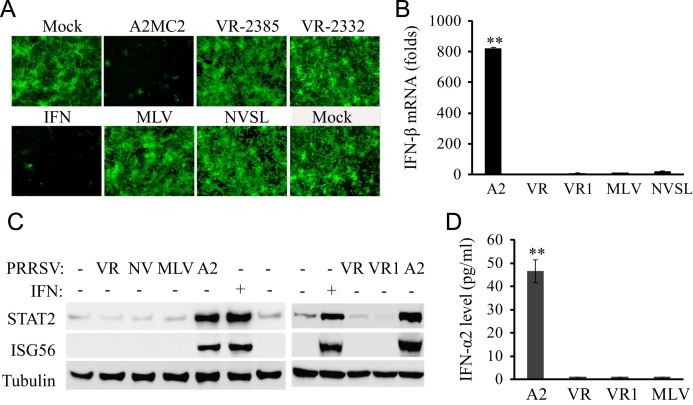
Fig. 5.
Comparison of A2MC2 to other PRRSV strains in IFN production using MARC-145 cells. (A) IFN bioassay in Vero cells. Cell culture supernatants from MARC-145 cells infected with an MOI of 1 TCID50 each of PRRSV strains A2MC2, VR-2385, VR-2332, MLV, or NVSL, respectively, were collected at 36 hpi. Vero cells were treated with 1:4 dilution of the respective supernatants for 12 h, and then infected with NDV-GFP. Fluorescence microscopy was conducted at 24 hpi. Treatment with IFN-α was included as a positive control. (B) IFN-β expression in MARC-145 cells detected by real-time RT-PCR. The cells were infected with PRRSV and harvested for detection of IFN-β transcript. Relative fold of induction in comparison with uninfected cells are shown. Error bars represent variation of three repeated experiments. Significant difference between A2MC2 and the rest of the samples is denoted by “**”, which indicates P<0.01. A2: A2MC2; VR: VR-2385; VR1: VR-2332. (C) STAT2 and ISG56 protein level in MARC-145 cells detected by Western blotting. Treatment of uninfected cells with IFN-α was included as a positive control. A2: A2MC2; VR: VR-2385; NV: NVSL; VR1: VR-2332. (D). IFN-α2 level in culture supernatants of MARC-145 cells infected with A2MC2, VR-2385, VR-2332, and MLV, respectively. ELISA analyses were conducted to quantify the IFN-α2 levels and concentrations were calculated on the basis of a standard curve. The significant difference between A2MC2 and the rest of the samples is denoted by “**”, which indicates P<0.01.