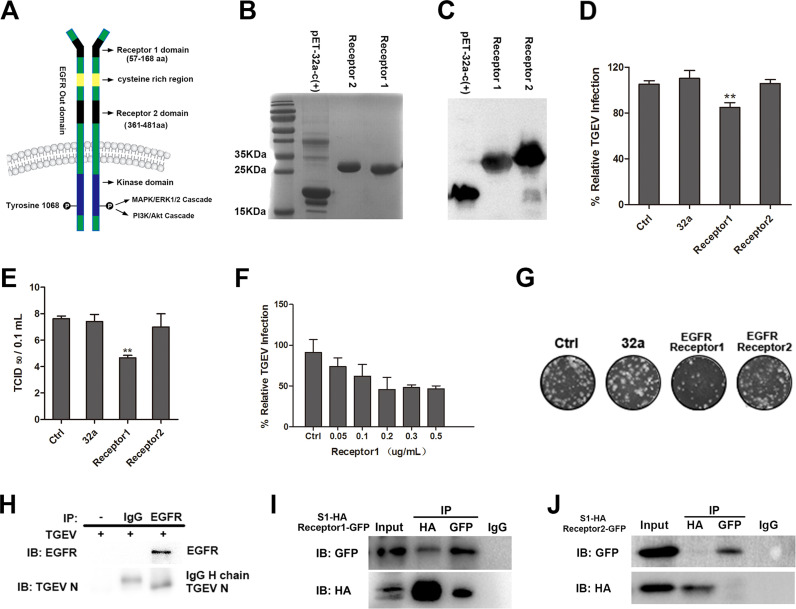
Fig. 1.
Interaction between TGEV S1 protein and EGFR extracellular receptor binding domain 1. (A) Structure of EGFR. (B) His-tagged EGFR extracellular receptor binding domain 1 or 2 expressed in E.coli BL21 and purified in Ni-NTA columns, the purified products were separated using SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (C) The purified EGFR extracellular receptor-binding domain 1 or 2 were verified by Western-blot. (D) TGEV (MOI = 2) was incubated in DMEM containing His-32a, His-EGFR Receptor 1 or His-EGFR Receptor 2 at 37 °C for 2 h, then incubated with IPEC-J2 cells and cultured for 1 h. The invasion of TGEV was detected by RT-PCR. (E) TGEV (MOI = 2) was incubated in DMEM containing His-32a, His-EGFR Receptor 1 and His-EGFR Receptor 2 at 37 °C for 2 h, then incubated with IPEC-J2 cells, and cultured for 1 h, the viral titers of intracellular TGEV were analyzed by tissue culture infectivity dose 50 TCID50. (F) IPEC-J2 cells were pretreated with His-EGFR Receptor 1 at different concentrations at 37 °C for 2 h, then incubated with IPEC-J2 cells, and cultured for 1 h. The invasion of TGEV was detected by RT-PCR. (G) Intracellular TGEV were analyzed by viral plaque morphology in ST cells. (H) The lysates of TGEV-infected IPEC-J2 cells were immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti-EGFR or normal Rabbit IgG. Immunoblotting was then performed to determine the presence of EGFR and TGEV in the EGFR immunoprecipitate. (I and J) 293T cells were co-transfected with a HA-tagged TGEV S1 expression plasmid together with GFP-tagged EGFR Receptor 1 or GFP-tagged EGFR Receptor 2 expression plasmid, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody or an anti-GFP antibody, the resulting precipitates were examined by immunoblotting using an anti-HA or an anti-GFP antibody to examine the interaction between HA-TGEV S1 and GFP-tagged EGFR. (** p < 0.01).