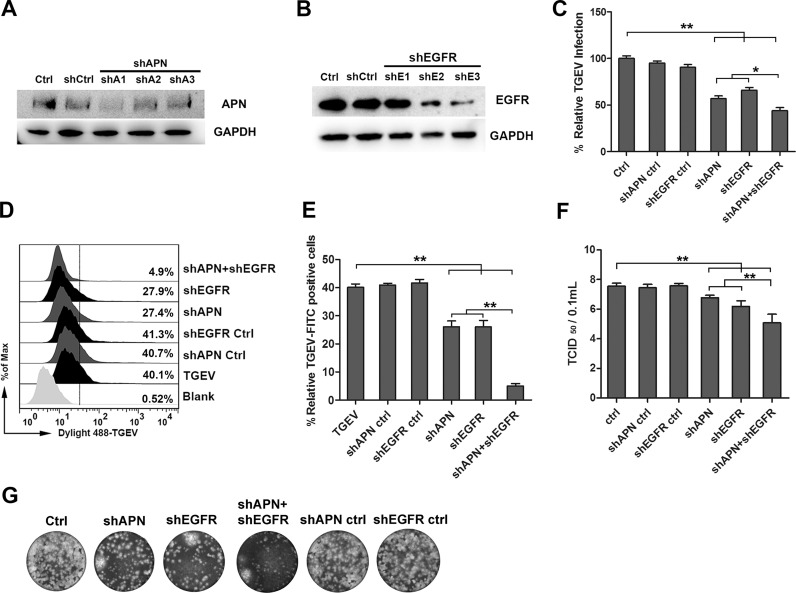
Fig. 3.
APN and EGFR synergistically promote TGEV invasion. (A and B) APN and EGFR interference verification, shAPN1 and shEGFR3 were later used in the subsequent experiments. (C) IPEC-J2 cells were transfected with interference vector pLVX-shRNA-APN, pLVX-shRNA-APNCtrl, pLVX-shRNA-EGFR, pLVX-shRNA-EGFRCtrl, or pLVX-shRNA-APN + pLVX-shRNA-EGFR through lentiviral supernatant. Normal cells served as controls. Cells were infected with TGEV at an MOI of 2, and cultured for 1 h. The invasion of TGEV was detected by RT-PCR. (D and E) IPEC-J2 cells were infected with Dylight 488-TGEV, and cultured for 1 h The invasion of TGEV was detected by Flow cytometry. (F) The viral titers of intracellular TGEV were analyzed by TCID50. (G) Intracellular TGEV was analyzed by viral plaque morphology in ST cells. The data shown are the mean results ± SD from three independent experiments. (* 0.01 < p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).