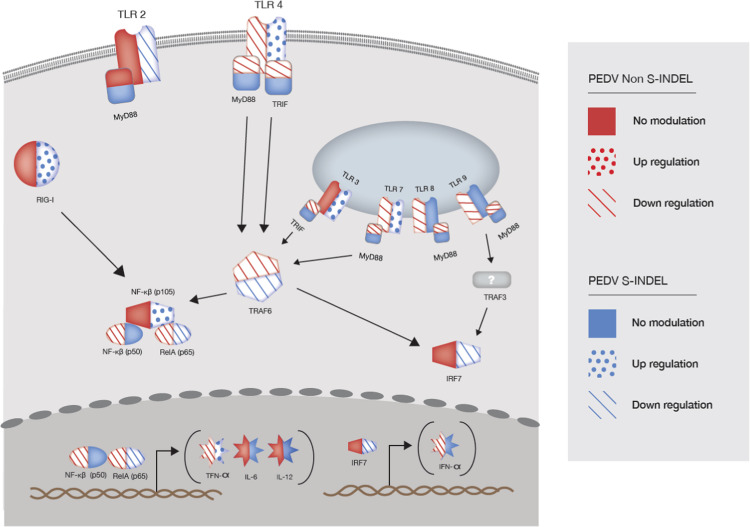
Fig. 7.
Differential gene modulation of pattern-recognition receptor TLR and RIG-I-like, and downstream mediators on intestinal mucosa of pigs infected with PEDV non S-INDEL and PEDV S-INDEL strains. This figure present differential gene modulation at day post-infection (dpi) 3. PEDV non-S-INDEL infection suppressed the induction of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and type 1 interferon production (IFN- α) through the down regulation of the cytoplasmic membrane and endosomal TLRs (TLR4, TLR7/8, TLR9), and TLR-downstream signaling molecules (MyD88/TRIF and TRAF6). Although the expression levels of both p50 and p65 were down-regulated after infection with the PEDV non-S-INDEL strain, the down-regulatory effect on MyD88 and TRIF gene pathways did not negatively affect the expression of NF-κB ( ). Contrary, PEDV S-INDEL infection induced a positive modulatory effect on TLR3, TLR4, and TLR7 gene expression. However, no significant modulatory effect was observed in the levels of TRIF, and MyD88, genes. PEDV S-INDEL infection induced the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, and interleukin (IL)−12 through the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway by the activation of the intracytoplasmic RIG-I receptor (
). Contrary, PEDV S-INDEL infection induced a positive modulatory effect on TLR3, TLR4, and TLR7 gene expression. However, no significant modulatory effect was observed in the levels of TRIF, and MyD88, genes. PEDV S-INDEL infection induced the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, and interleukin (IL)−12 through the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway by the activation of the intracytoplasmic RIG-I receptor ( ).
).