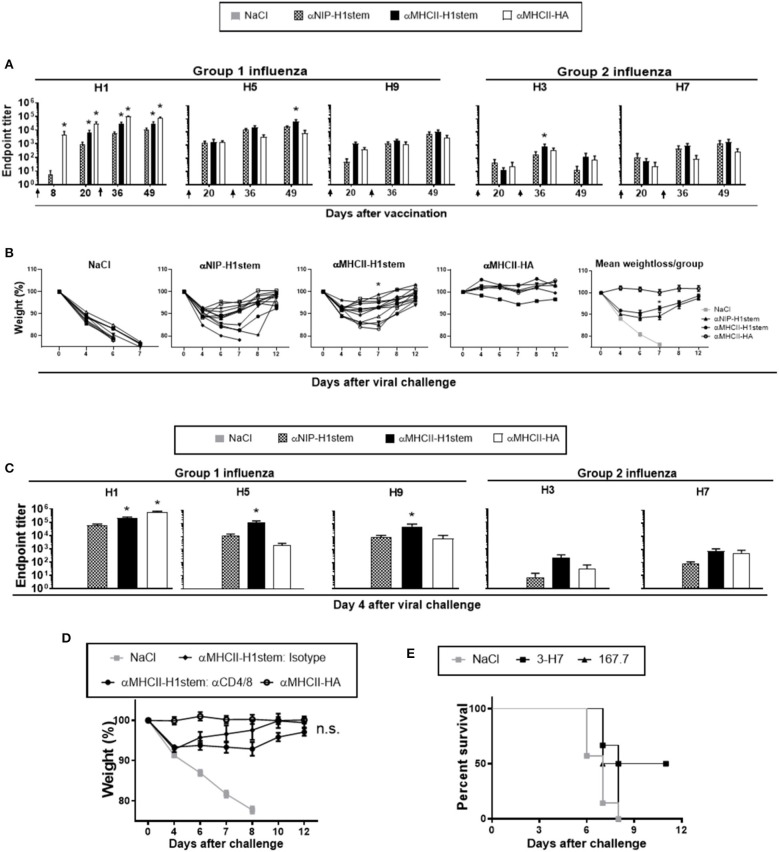
Figure 2.
Induction of cross-reactive and protective antibodies against influenza. (A–C) BALB/c mice (n = 11–12 mice/group, except n = 6 for the αMHCII-HA group) were DNA-immunized twice on days 0 and 21, as indicated by arrows. (A) Sera were analyzed for development of IgG responses against recombinant HA from PR8, A/Hong Kong/1/1968 (H3N2), A/Hong Kong/483/97 (H5N1), A/Shanghai/1/2013 (H7N9), and A/Hong Kong/1073/99 (H9N2). A vaccine encoding full-length HA, αMHCII-HA, was included as positive control. Values given are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 as compared to αNIP-H1stem (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-test). (B) 4 weeks after the final vaccination, mice were challenged with a 5 × LD50 dose of influenza PR8 and monitored for weight loss. *p < 0.05 for αMHCII-H1stem as compared to αNIP-H1stem (Mann–Whitney test). (C) Sera were harvested on day 4 after the influenza challenge and assayed for specific IgG responses against HA from PR8, A/Hong Kong/1/1968 (H3N2), A/Hong Kong/483/97 (H5N1), A/Shanghai/1/2013 (H7N9), and A/Hong Kong/1073/99 (H9N2) in ELISA. Values given are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 as compared to αNIP-H1stem (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-test). (D) BALB/c mice were immunized twice (day 0 and 21) and then injected every other day with depleting mAbs against CD4+- and CD8+-T cells starting from day 48 (n = 7 for αMHCII-HA, n = 8 for isotype treated, n = 11 for CD4/8 depleted, and n = 10 for NaCl). At day 50, mice were challenged with a 5 × LD50 dose of influenza PR8, and monitored for weight loss. (E) Hybridomas were generated after vaccination with αMHCII-H1stem (S5). Survival of BALB/c mice that were treated i.v. with monoclonal IgM 3-H7 specific for the HA stem or a matched isotype control (167.7), and challenged 24 h later with a 5 × LD50 dose of influenza PR8.