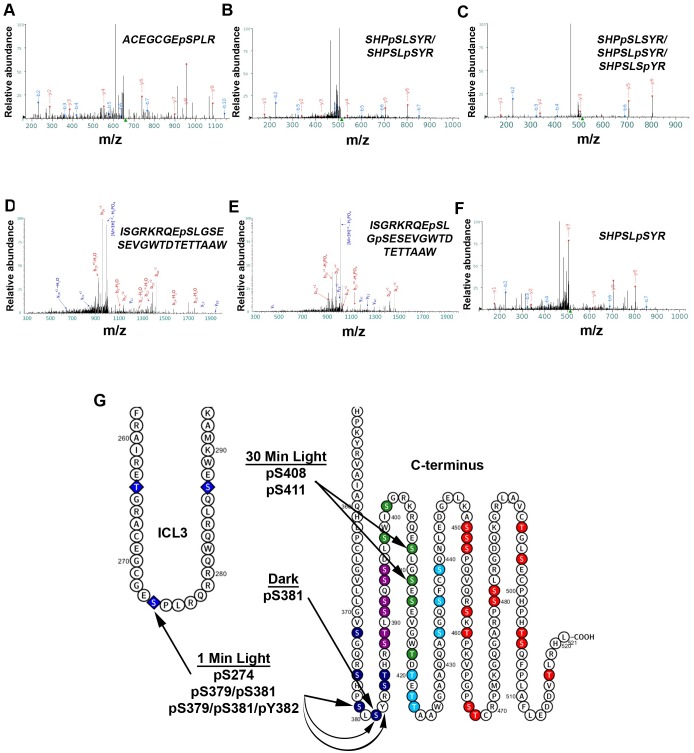
Fig 7. Mass spectrometry of light-exposed melanopsin and dark-adapted melanopsin reveals C-terminus phosphorylation, and cytoplasmic loop phosphorylation.
Annotated fragmentation spectra of two phosphopeptides detected after LC/MS/MS of affinity purified melanopsin expressed in HEK293 cells, following a 1-min (A-C) and 30-min (D-E) white light exposure and after dark-adaptation with no light exposure (F). (A) Spectrum of phosphopeptide 267ACEGCGEpSPLR277, (B) 376SHPpSLSYR383/376SHPSLpSYR383, and (C) 376SHPpSLSYR383/376SHPSLpSYR383/376SHPSLSpYR383 suggest cytoplasmic loop 3 and proximal C-terminus phosphorylation following 1-minute of light exposure. Amino acids in the phosphopeptides in (B) and (C) were not confidently assigned to single amino acid(s), thus all the sites described in each phosphopeptide represent possible phosphorylations. (D) Spectrum of phosphopeptide 400ISGRKRQEpSLGSESEVGWTDTETTAAW426 and (E) spectrum of phosphopeptide 400ISGRKRQEpSLGpSESEVGWTDTETTAAW426 both suggest distal C-terminus phosphorylation following a prolonged, 30-min light exposure. (F) Spectrum of phosphopeptide 376SHPSLSpYR383 suggesting phosphorylation of S381 in the dark. (G) Summary of the findings on an abbreviated secondary structure of mouse melanopsin.