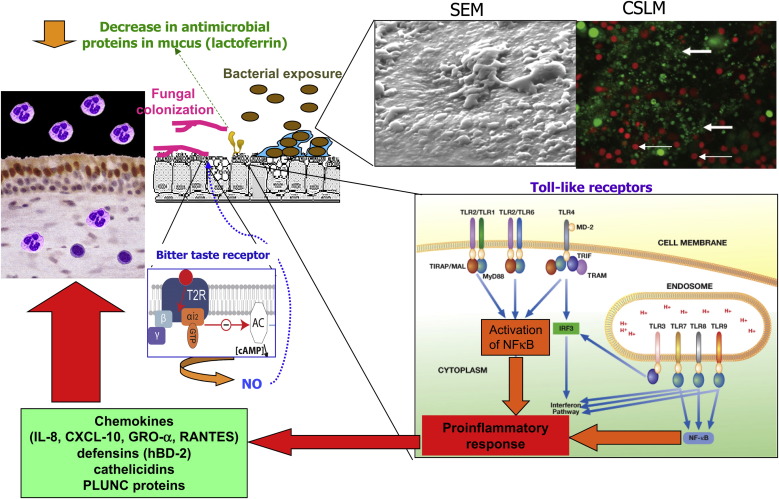
Fig 2.
Salient features of host-microbial interactions involved in triggering innate immune responses in patients with CRS. TLR signaling pathways induce proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine production. Bitter taste receptor is activated by a quorum-sensing molecule from P aeruginosa and stimulates production of NO, which then stimulates mucocociliary clearance and has direct antimicrobial effects. Depiction of the intracellular TLR signaling pathways was adapted from the IAVI Report (http://www.iavireport.org/Back-Issues/Pages/IAVI-Report-9(4)-TollBridgetoImmunity.aspx). Upper right inset (left panel), SEM of bacterial biofilm showing characteristic glycocalyx and water channels. The photograph was used with permission from Sanclement et al.29Right panel, CSLM image (×63 magnification) of a patient with CRS stained with the BacLight LIVE/DEAD kit (Invitrogen, Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, Calif) demonstrating a bacterial biofilm comprised of many intensely fluorescing live bacteria organized in clusters (large arrow). Small arrows designate the larger live and dead epithelial cells. Used with permission from Psaltis et al.18 The bitter taste receptor depicted in the small middle inset was adapted from Fenech C, Patrikainen L, Kerr DS, Grall S, Liu Z, Laugerette F, et al. Ric-8A, a Gα protein guanine nucleotide exchange factor potentiates taste receptor signaling. Front Cell Neurosci 2009;3:11.128