Fig. 7.
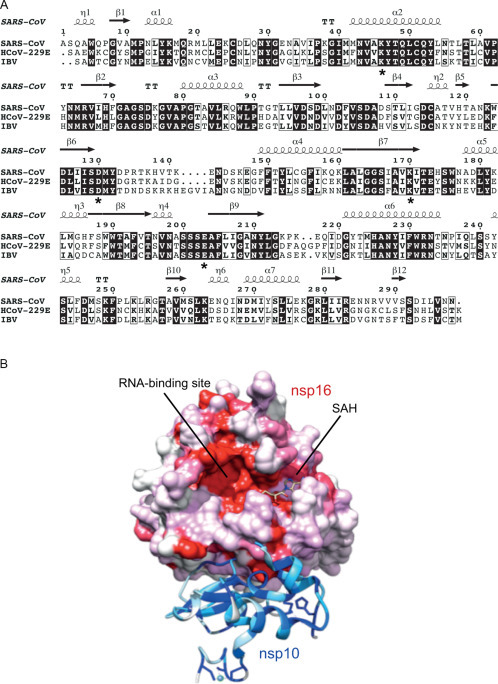
Coronavirus nsp16 and its interaction with nsp10. (A) Sequence alignment of nsp16 homologs of SARS-CoV (genus Betacoronavirus), HCoV-229E (genus Alphacoronavirus), and IBV (genus Gammacoronavirus). The alignment was generated using Clustal Omega (Sievers et al., 2011) and rendered using ESPript version 3.0 (Robert and Gouet, 2014). Residues of the catalytic tetrad K–D–K–E are indicated by asterisks and secondary structure elements of SARS-CoV nsp16 (pdb 2XYV) are shown. (B) Surface representation of the three-dimensional structure of the nsp10/nsp16 complex (pdb 2XYV). Nsp10 is shown in ribbon representation with conserved residues colored in dark to light blue according to their conservation among CoVs. Zinc molecules are shown as spheres and zinc-coordinating residues are shown in stick representation. The surface of nsp16 is colored in dark to light red according to the conservation of the respective residues among coronaviruses. SAH is depicted in a stick model. The figure was generated using UCSF Chimera (Pettersen et al., 2004). The degree of conservation of specific residues was determined using an alignment of nsp10 and nsp16 sequences of eight coronaviruses (see Fig. 6).
