Figure 3.
Formation of Oxidized Phospholipids in Acute Lung Injury
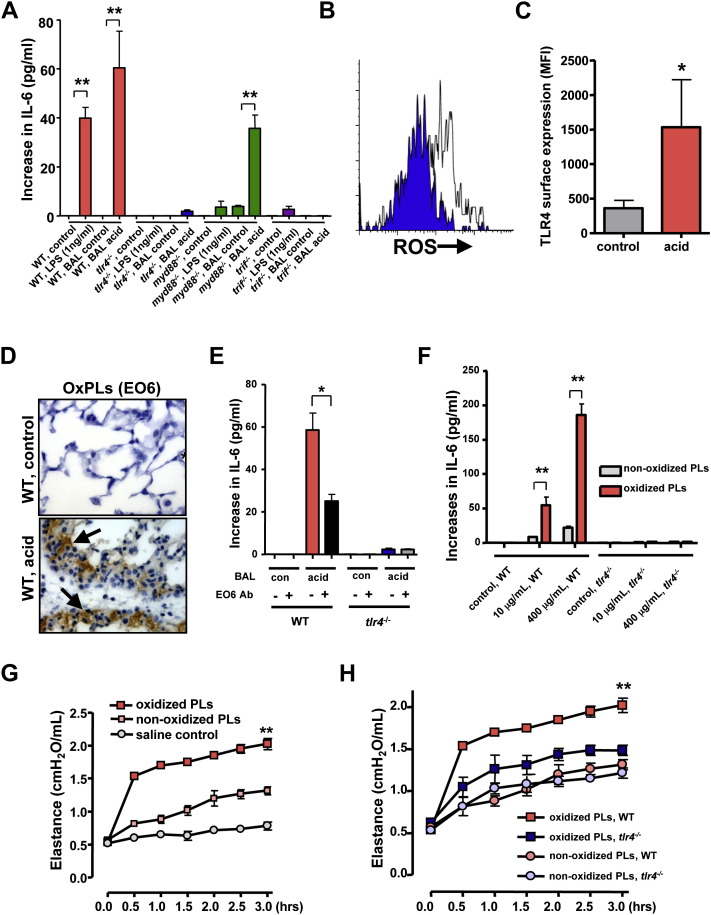
(A) Increase in IL-6 production from baseline in WT, tlr4−/−, myd88−/−, and trif−/− alveolar macrophages treated with LPS, BAL fluid from normal control, or BAL fluid from acid-treated WT mice. ∗∗p < 0.01. Data are from four separate experiments.
(B) Increases in ROS expression in alveolar macrophages obtained from WT mice 60 min after treatment with saline (background control, blue) or acid (white). A representative histogram is shown among five separate experiments.
(C) Increased TLR4 surface expression in alveolar macrophages from WT mice treated with saline (control) or acid. Data are from five separate experiments. ∗p < 0.05.
(D) Immunohistochemistry for OxPLs detected by the mAb EO6 in lungs of saline-treated control (upper panel) and acid-treated WT mice (lower panel). OxPLs were localized to inflammatory exudates lining the injured alveoli (arrows) in acid-treated lungs. Original magnifications × 400. Lungs were analyzed 3 hr after acid treatment.
(E) BAL fluid from acid-treated mice (BAL acid) induces large amounts of IL-6 in WT but not tlr4−/− alveolar macrophages. BAL fluid plus an isotype-matched control Ab was compared to BAL fluid plus the mAb EO6. ∗p < 0.05. Data are from four separate experiments.
(F) Increase in IL-6 from baseline in peritoneal macrophages isolated from WT and tlr4−/− mice in response to nonoxidized PLs or oxidized PLs. ∗∗p < 0.01.
(G) Lung elastance in WT mice following intratracheal administration of saline, nonoxidized PLs, and oxidized PLs. n = 4–6 for each group. ∗∗p < 0.01 for the whole time course.
(H) Lung elastance in WT and tlr4−/− mice following treatment with nonoxidized PLs or oxidized PLs. n = 4 for each group. ∗∗p < 0.01 for the whole time course.
Data in (A), (C), and (E)–(H) are mean values ± SEM.