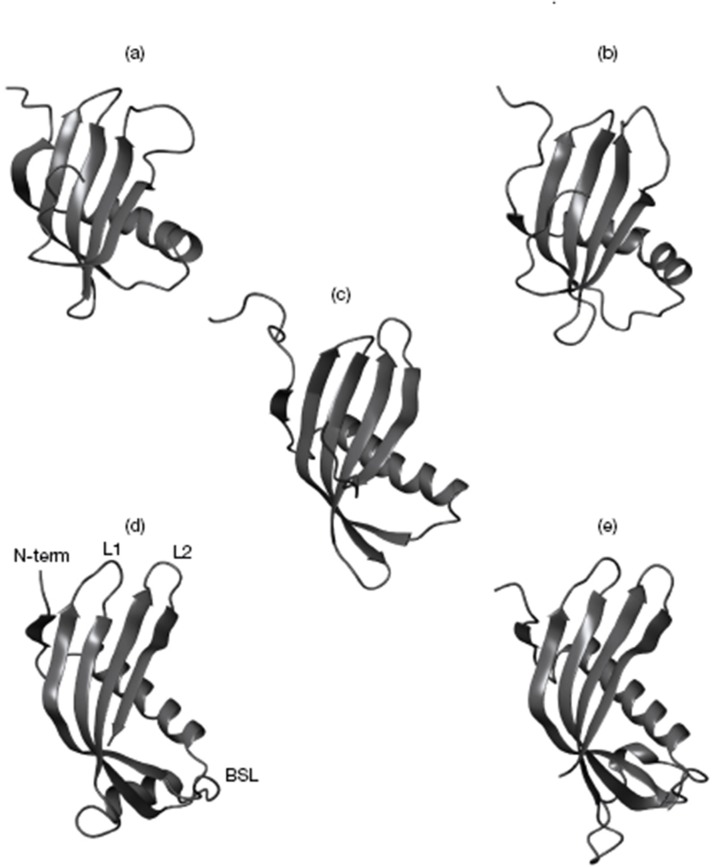
Fig. 7.
Cystatin structures: The cystatin structures known from X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy studies are illustrated. (a) Human cystatin A (PDB code 1dvd) (Ni et al., 1998); (b) human cystatin B (1STF) (Stubbs et al. [159]); (c) oryzacystatin from rice (1EQG) (Nagata et al., 2000); (d) CEW cystatin (1CEW) (Bode et al. [162]); (e) theoretical cystatin C monomer, obtained by cutting the structure of the human cystatin C dimer (1G96) (Janowski et al., 2001) in half and modelling the L1 loop. The cystatin parts responsible for C1 peptidase binding and inhibition are indicated: the N-terminal segment (Nterm), the first (L1) and second (L2) hairpin loops. Also indicated is the BSL involved in the inhibition of leguman-like (family C13) cysteine peptidases (Abrahamson et al., 2003).