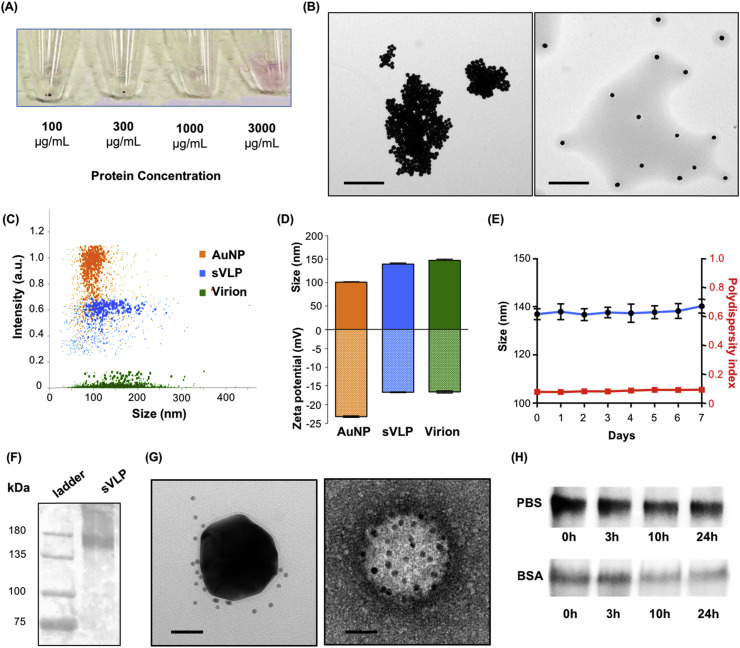
Fig. 2.
Preparation and characterizations of sVLPs. (A) Visualization of nanoparticle solutions following incubation with and isolation from different concentrations of IBV spike proteins. (B) TEM visualization of nanoparticles prepared with a low protein concentration (1000 μg/mL; left) and sVLPs prepared with a high protein concentration (3000 μg/mL; right). Scale bars = 1 μm. (C) Particle-by-particle examination of AuNPs, sVLPs, and native IBV virions under nanoparticle tracking analysis. (D) Size and zeta potential of AuNPs, sVLPs, and native IBV virions as analyzed by nanoparticle tracking analysis. Bars represent means ± s.d. (n = 3). (E) sVLP stability in PBS observed over 7 days. Bars represent means ± s.d. (n = 3). (D) Western blotting analysis confirms the presence of IBV spike proteins on sVLPs. (E) Transmission electron microscopy of sVLPs (left) and native IBV virions (right) following immunogold staining against IBV spike proteins. Scale bars = 50 nm. (H) Western blotting analysis of IBV spike protein retention on sVLPs following different incubation periods in PBS or in 10% BSA.