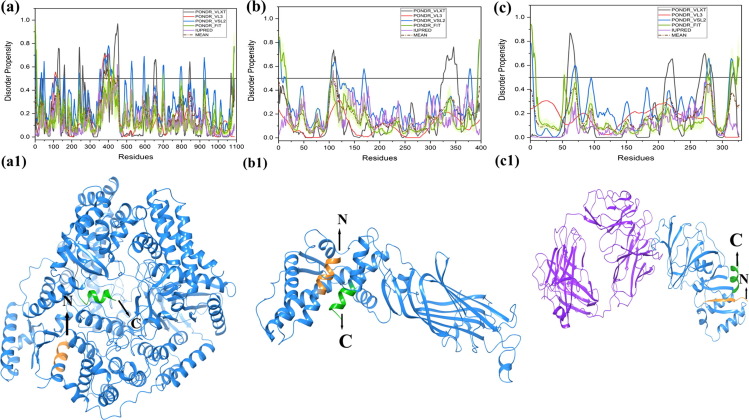
Fig. 2.1.
Schematic illustration of the structural and intrinsic disorder characteristics of rotaviral structural proteins. The outpus of PONDR® VL-XT, PONDR® VL3, PONDR® VSL2, PONDR® FIT, and IUPred predictors are shown by black, red, blue, olive, and violet colors, respectively, whereas short dashed lines of wine color represent the mean disorder. Light olive shadow around PONDR® FIT curves represents the error distribution. The Morf regions is shown in grey color in the RdRp protein structure (a1). Plots signify disorder status of (a) 1,088 residue-long RdRp/VP1 that contains several IDPRs at its N-terminus; (b) 397 residue-long VP6 that possesses several IDPRs at its N- and C-terminal regions; (c) 326 residue-long VP7 is characterized by the presence of an IDPR at its N-tail and several IDPRs within the C-terminal domain. X-ray crystal structres are shown for RdRp protein (PDB ID: 2R7Q) (a1), VP6 protein (PDB ID: 1QHD) (b1), and VP7 protein (PDB ID: 3FMG) is structurally determined in complex with light and heavy chains of Fab of neutralizing antibody 4F8 (c1). The N and C-terminals are denoted in orange and green colors with arrows respectively. Sequence of experimentally determined structure is shown (disordered residues in red color). Some residues are missing in the structures that are shown in plum color in the sequence.