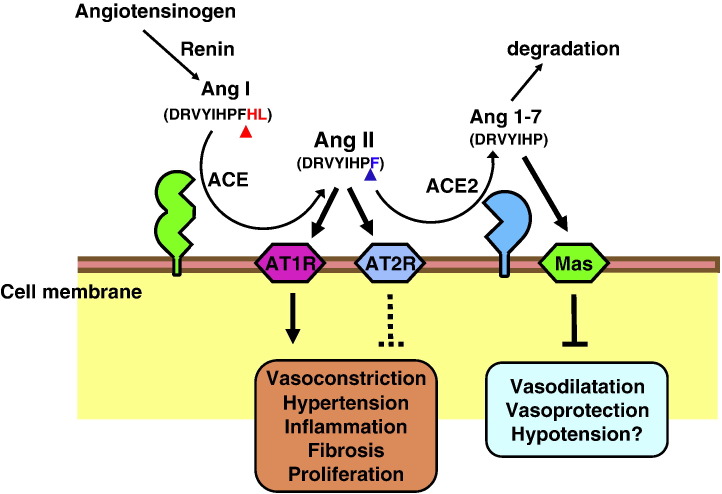
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram of the role of ACE2 in the renin–angiotensin system. Angiotensin I (Ang I; DRVYIHPFHL) serves as a substrate for ACE, a dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase, and is converted to Angiotensin II (Ang II; DRVYIHPF), the main active peptide of the classical RAS. ACE2 catalyzes and inactivates Angiotensin II and produces the vasodilator peptide Angiotensin 1–7 (Ang 1–7; DRVYIHPF), which binds the Mas receptor and/or is degraded to inactive peptides. Red arrowheads indicate the ACE cleavage site; blue arrowheads show the ACE2 cleavage sites. It should be noted that ACE2 is an unspecific protease and can cleave multiple additional substrates such as Apelin.