Fig. 1. Met-binding DNA aptamers and their nuclease stability.
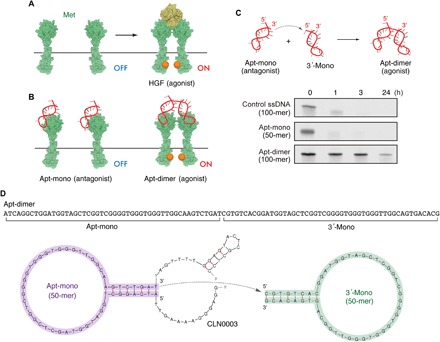
(A and B) Schematic representation of HGF-induced Met activation and the Met activation potential of the Apt-mono and the Apt-dimer. (C) (Top) Schematic representation of the oligonucleotides used in the present work. (Bottom) Nuclease stability of the oligonucleotides in serum. Each oligonucleotide (2 μM) was incubated in PBS containing 50% FBS at 37°C. (D) Sequence and predicted secondary structure of the aptamers used in the present work. The sequence of the Apt-mono (purple) was identified as the minimal binding motif of a Met-binding aptamer (CLN0003) reported previously (22). The Apt-dimer [termed “ss-0” in a previous work (11)] was designed as a tandem dimer of the Met-binding aptamer, as depicted in the figure. The stem sequence of the 3′-mono (green) was replaced with an alternative complimentary sequence to prevent the misfolding of the aptamer.
