Fig. 2. Design of an unfunctional mutant of the Apt-dimer (G4 mutant) and microdistribution of the oligonucleotides in liver tissues.
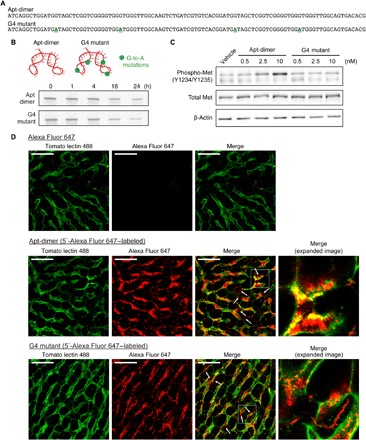
(A) Sequences of the oligonucleotides used in the experiments depicted in Fig. 2. The four G-to-A mutations of the G4 mutant are highlighted. (B) Nuclease stability of the Apt-dimer and G4 mutant. Each oligonucleotide (2 μM) was incubated in PBS containing 50% FBS at 37°C. After incubation, the samples were immediately analyzed using denaturing 15% PAGE. (C) Western blotting analysis of the phosphorylation level of Met in SCCVII cells after 15 min of incubation with oligonucleotides. (D) Confocal imaging of liver tissues. Alexa Fluor 647 carboxylic acid (0.5 nmol) or a 5′-Alexa Fluor 647–labeled oligonucleotide (0.5 nmol) was intravenously injected (red). Blood vessels were visualized by injecting 25 μg of DyLight 488–conjugated tomato lectin (green). Ten minutes after the oligonucleotide injection, the liver was excised and observed directly using a confocal laser scanning microscope. Scale bars, 50 μm.
