Fig. 5. Agonistic functions and therapeutic potential of the HGF-mimic aptamer.
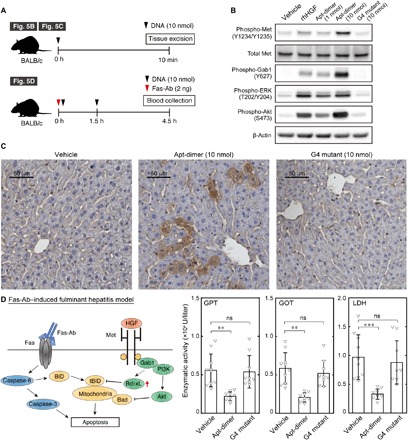
(A) Schematic representation of the experimental outlines. (B) Immunoblotting analysis of Met activation in mouse livers after intravenous injection of recombinant human HGF (rhHGF) or oligonucleotides. The liver was excised 10 min after the intravenous injection of rhHGF (1 μg) or oligonucleotides (1 to 10 nmol). (C) Immunohistochemistry of Met activation in the mouse liver after intravenous injection of the oligonucleotides. The liver was excised 10 min after the intravenous injection of oligonucleotides (10 nmol). (D) (Left) Schematic representation of the apoptotic signal induced by Fas-Ab and the antiapoptotic signal induced by Met activation. (Right) Effect of Apt-dimer administration on a fulminant hepatitis mouse model. An anti–Fas-Ab (2 ng) was co-injected with vehicle control (n = 10), Apt-dimer (10 nmol, n = 9), or G4 mutant (10 nmol, n = 9) intravenously. The oligonucleotide (10 nmol) was administered 1.5 hours later. The average activity of glutamate pyruvate transaminase (GPT), glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is shown with error bars (SD). Statistical significance was examined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant).
