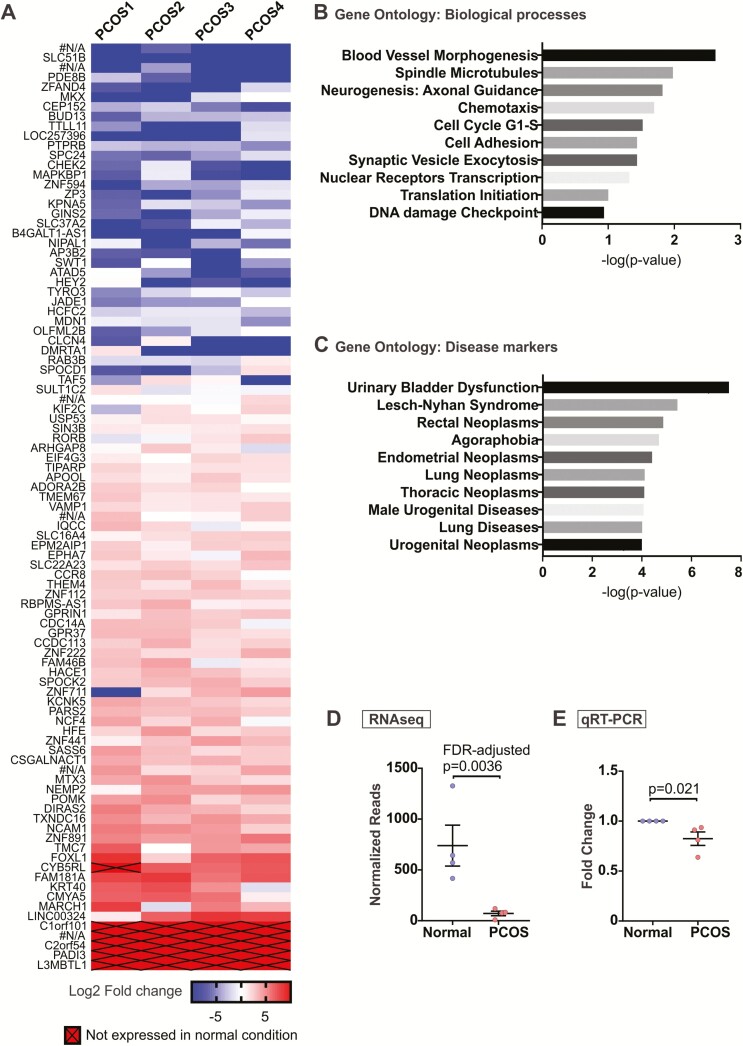
Figure 5.
Differential gene expression in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) organoids. Endometrial organoids from normal versus PCOS hormone conditions were harvested at the end of 14 days. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) was isolated and RNA-sequencign (RNA-seq) was performed. (A) A total of 95 possible genes (false discovery rate–adjusted P-value < .05) were differentially expressed in PCOS organoids compared to those cultured in normal hormone condition based on RNA-seq analysis. Of these, 6 were unannotated genes with no known functions (#N/A). Genes with no expression in PCOS organoids were arbitrarily assigned a value of –10 on this log2 scale. Four separate sets of organoids obtained from n = 4 patients were used for RNA-seq. (B, C) Gene ontology analysis was performed using GeneGo to determine key pathways and biological processes (B) and disease markers (C) involving genes differentially expressed in PCOS organoids. (D) Normalized reads for BUD13 from the RNA-seq were plotted to compare with (E) quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for relative BUD13 transcript levels in normal versus PCOS organoids obtained from 4 new patients, which was done for validation purposes.